算法笔记 1.第一章 基础算法 时间复杂度 重视思想
好的方法 课下 模板(重复3-5次)思想理解会背 然后做题目
根据数据量猜解法
常数指令 一次a+b ,i ++这种就是,假如给你一个1e6长度的数组,用n^2的算法的话,数据量就成了1e12,我们设计的算法肯定不能超过1e7~1e8,假如用n*log2 n ,算下来也就是1e7多一点,未必能超,也许能行。假如是1e3长度,那么n2也行。
注意:上面使用技巧的必要条件↑
枚举 数对问题 https://leetcode.cn/problems/number-of-good-pairs/ 统计好数对
https://leetcode.cn/problems/count-number-of-bad-pairs/description/ 统计坏数对 双周赛80+
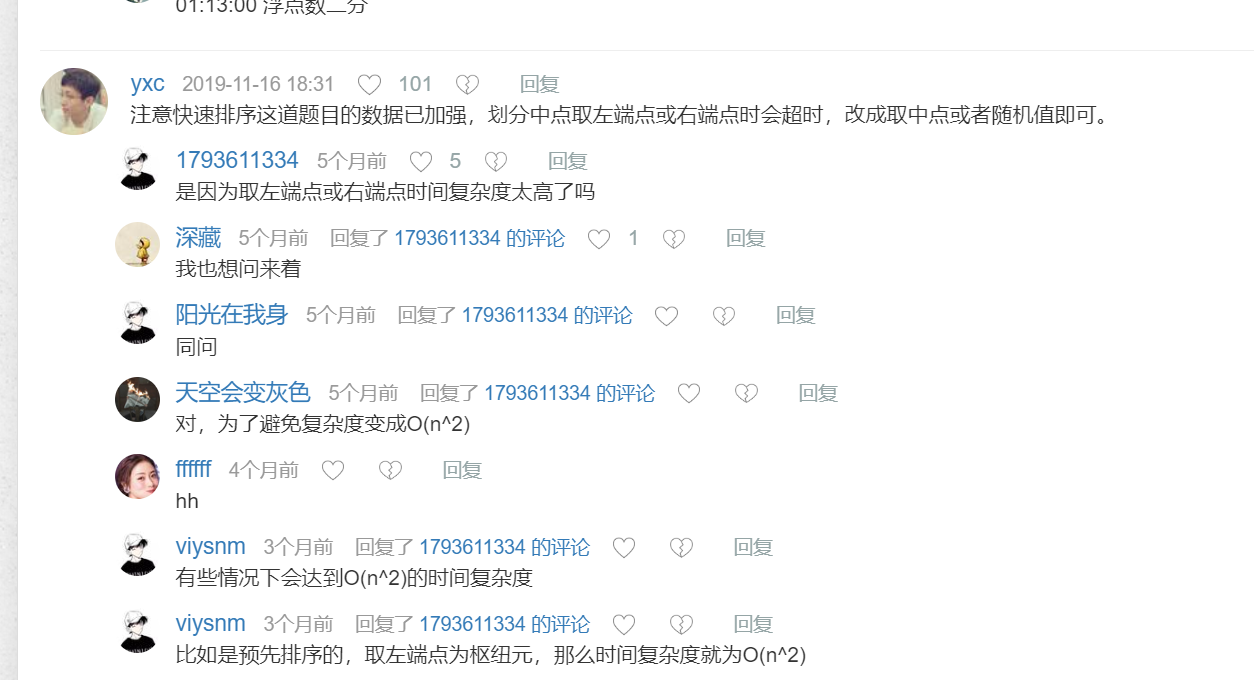
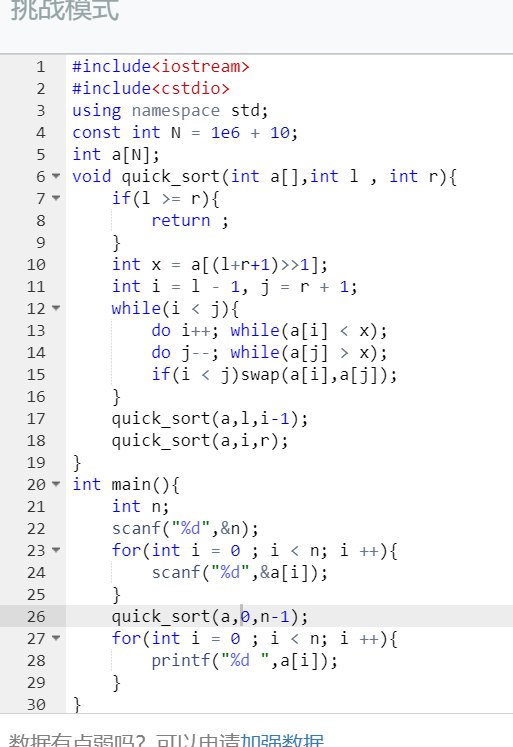
快速排序
用这个就行,防止边界问题
归并排序 思想也是分治,但是方法不一样
先划分区间,再合并
最后那个for是把temp拷贝回去 temp是记录递归排序的数组,每一步都在改变,不能最后直接输出temp
#include <iostream> using namespace std;int a[100010 ];int t[100010 ];void merge_sort (int a[], int l, int r) if (l >= r) return ; int mid = (l+r)>>1 ; merge_sort (a,l,mid); merge_sort (a,mid+1 ,r); int k = 0 ; int i = l, j = mid + 1 ; while (i <= mid && j <= r){ if (a[i] < a[j]) temp[k++] = a[i++]; else temp[k++] = a[j++]; } while (i <= mid) temp[k++] = a[i++]; while (j <= r) temp[k++] = a[j++]; k = 0 ; for (int i = l; i <= r; i++){ a[i] = temp[k++]; } } int main () int n; scanf ("%d" ,&n); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i ++){ scanf ("%d" ,&a[i]); } merge_sort (a,0 ,n-1 ); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i ++){ printf ("%d " ,a[i]); } }
例题 逆序对 https://www.acwing.com/solution/content/5103/讲解很好
分治
计数排序 桶排序 例题洛谷P7020,适用情况,要排序的数字值域小,但是n很大的情况,sort和快排这些适合值域大小都可以,n小点的情况
二分 https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P6174
https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P5815 扑克牌[绿题] 二分答案
https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P1843 二分答案
https://www.acwing.com/solution/content/3338/ 数的范围讲解很好
#include <algorithm> #include <iostream> using namespace std;const int N = 1e5 + 10 ;int q[N];int SL (int l, int r, int x) while (l < r) { int mid = l + r >> 1 ; if (q[mid] >= x) r = mid; else l = mid + 1 ; } return l; } int SR (int l, int r, int x) while (l < r) { int mid = l + r + 1 >> 1 ; if (q[mid] <= x) l = mid; else r = mid - 1 ; } return r; } int main () int n,m; scanf ("%d%d" ,&n,&m); for (int i=0 ;i<n;++i) scanf ("%d" ,&q[i]); while ( m-- ) { int x; scanf ("%d" ,&x); int l = SL (0 , n - 1 , x); if (q[l]!=x) cout <<"-1 -1" <<endl; else { cout << l << ' ' ; cout << SR (0 , n - 1 , x) << endl; } } return 0 ; }
浮点数二分算法模板 —— 模板题 AcWing 790. 数的三次方根 bool check (double x) double bsearch_3 (double l, double r) const double eps = 1e-6 ; while (r - l > eps) { double mid = (l + r) / 2 ; if (check (mid)) r = mid; else l = mid; } return l; }
有经验,就是假如题目要求4位的话,最好-6,就是比要求的多两位,保证没问题
二分答案 lower_bound( )和upper_bound( ) https://blog.csdn.net/qq_40160605/article/details/80150252
例题 https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/732/
#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> using namespace std;int n;int maxH = -1 ;int h[100005 ];bool success (int x) int temp = x; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { temp += temp - h[i]; if (temp < 0 ) return false ; if (temp >= maxH) return true ; } return true ; } int main () scanf ("%d" , &n); for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { scanf ("%d" , &h[i]); maxH = max (maxH, h[i]); } int l = 0 , r = maxH; while (l < r) { int mid = l + r >> 1 ; if (success (mid)) { r = mid; } else { l = mid + 1 ; } } printf ("%d\n" , r); return 0 ; }
例题 刺杀大使https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P1902
例题 路标设置 https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P3853 和跳石头基本一样(二分求最优解)
高精度(略过) 贪心 模板题
https://www.acwing.com/activity/content/problem/content/1763/
https://www.acwing.com/activity/content/problem/content/1764/
(很常见的板子题,取中位数)
https://www.matiji.net/exam/brushquestion/3/4347/179CE77A7B772D15A8C00DD8198AAC74
(用二分答案找时间,check部分贪心一下)
https://www.acwing.com/activity/content/problem/content/1766/
https://www.acwing.com/activity/content/problem/content/1768/
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/1226/
https://pintia.cn/problem-sets/994805342720868352/exam/problems/994805403651522560?type=7&page=0
https://pintia.cn/problem-sets/994805342720868352/exam/problems/994805350316752896?type=7&page=1
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/127/ 耍杂技的牛(证明搞懂了!)
https://www.acwing.com/activity/content/problem/content/1111/ 区间选点(模板,搞懂和区间合并的区别)
https://www.acwing.com/activity/content/problem/content/1112/ 和上面区间选点一样
https://www.acwing.com/solution/content/5749/ 这个文章讲得不错
https://www.acwing.com/activity/content/problem/content/1113/ 区间分组 (类比活动安排)
https://www.acwing.com/solution/content/8902/上题题解,非常妙
#include <iostream> #include <algorithm> using namespace std;const int N = 100100 ;int n;int b[2 * N], idx;int main () scanf ("%d" , &n); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i ++) { int l, r; scanf ("%d %d" , &l, &r); b[idx ++] = l * 2 ; b[idx ++] = r * 2 + 1 ; } sort (b, b + idx);int res = 1 , t = 0 ;for (int i = 0 ; i < idx; i ++){ if (b[i] % 2 == 0 ) t ++; else t --; res = max (res, t); } printf ("%d\n" , res);return 0 ;}
纸牌均分
https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P1106 删数问题 找到高峰就删
前缀和 例题 https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/description/4963/ 子串简写
一维前缀和 —— 模板题 AcWing 795. 前缀和S[i] = a[1] + a[2] + ... a[i]a[l] + ... + a[r] = S[r] - S[l - 1]
二维前缀和 —— 模板题 AcWing 796. 子矩阵的和
例题 K倍区间 https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/description/1232/
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;typedef long long LL;const int N = 100010 ;int n,k;LL A[N]; LL s[N],cnt[N]; LL res; int main () scanf ("%d %d" ,&n,&k); cnt[0 ] = 1 ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i ++){ scanf ("%lld" ,&A[i]); s[i] = s[i - 1 ] + A[i]; s[i] = s[i] % k; res += (cnt[s[i]]); cnt[s[i]] ++; } printf ("%lld\n" ,res); return 0 ; } 作者:Safe_Sound 链接:https: 来源:AcWing 著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
例题 https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P3406
差分 一维差分 —— 模板题 AcWing 797. 差分
二维差分 —— 模板题 AcWing 798. 差分矩阵
#include <iostream> using namespace std;const int N =1010 ;int a[N][N],b[N][N];int n, m ,q;void insert (int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2, int c) b[x1][y1] += c; b[x2 + 1 ][y1] -= c; b[x1][y2 +1 ] -= c; b[x2 +1 ][y2+1 ] +=c; } int main () scanf ("%d%d%d" , &n, &m, &q); for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) for (int j = 1 ; j <= m; j++) scanf ("%d" , &a[i][j]); for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) for (int j = 1 ; j <= m; j++) insert (i, j, i, j, a[i][j]); while ( q-- ) { int x1, x2, y1, y2, c; cin >> x1 >> y1>> x2 >> y2 >> c; insert (x1,y1, x2, y2, c); } for (int i = 1 ; i<=n; i++) for (int j = 1 ; j<= m; j++) b[i][j] += b[i-1 ][j] +b[i][j-1 ] -b[i-1 ][j-1 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i<=n; i++) { for (int j = 1 ; j<= m; j++) printf ("%d " , b[i][j]); puts ("" ); } return 0 ; }
位运算(待更) 离散化
如果数据范围小的话(10的五次方以内)用前缀和也可
C++用vector作离散化
下面是去重函数的用法
https://blog.csdn.net/tjcwt2011/article/details/125281748?ops_request_misc=%257B%2522request%255Fid%2522%253A%2522169275072116800184115652%2522%252C%2522scm%2522%253A%252220140713.130102334..%2522%257D&request_id=169275072116800184115652&biz_id=0&utm_medium=distribute.pc_search_result.none-task-blog-2~all~baidu_landing_v2~default-1-125281748-null-null.142^v93^chatgptT3_1&utm_term=C%2B%2B%E5%8E%BB%E9%87%8D%E5%87%BD%E6%95%B0&spm=1018.2226.3001.4187
去重完用sort排序最后用二分查找(好像是先排序后去重
二分函数lower_bound(大于等于) upper_bound(大于)
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_51566349/article/details/128086465?ops_request_misc=&request_id=&biz_id=102&utm_term=lower_bound&utm_medium=distribute.pc_search_result.none-task-blog-2~all~sobaiduweb~default-1-128086465.nonecase&spm=1018.2226.3001.4187
https://www.acwing.com/solution/content/80100/这个代码解释非常详细
csdn的这个博客也很不错(11.11)
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_54773252/article/details/123286277?ops_request_misc=%257B%2522request%255Fid%2522%253A%2522169968370116800182120590%2522%252C%2522scm%2522%253A%252220140713.130102334.pc%255Fblog.%2522%257D&request_id=169968370116800182120590&biz_id=0&utm_medium=distribute.pc_search_result.none-task-blog-2~blog~first_rank_ecpm_v1~hot_rank-2-123286277-null-null.nonecase&utm_term=%E7%A6%BB%E6%95%A3%E5%8C%96&spm=1018.2226.3001.4450
区间合并 好多端点问题都是贪心
https://www.acwing.com/solution/content/2615/更新维护区间(很重要)
2.第二章 数据结构 链表和邻接表 单链表 用的最多的是邻接表
(存储图和树)
https://www.acwing.com/solution/content/16251/
双链表 添加的顺序不能反
邻接表 栈和队列 表达式求值(中缀 后缀)一般是二元(不包括符号)
单调栈 https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximal-rectangle/solutions/1861698/by-ac_oier-k02i/ 前缀和+单调栈
力扣 84 85 经典
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1dY4y1q7tL/?spm_id_from=333.788&vd_source=4452cbcad134fb17ec9cfb03a0acbdac 讲的真好
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/description/1415/
例题 https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P2947
例题 https://leetcode.cn/problems/daily-temperatures/description/
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1VN411J7S7/?spm_id_from=333.337.search-card.all.click&vd_source=4452cbcad134fb17ec9cfb03a0acbdac 灵神讲解很好
例题洛谷P2866
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;stack<int > st; int n;int main () cin >> n; long long ans= 0 ; long long cnt = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i <=n ; i ++){ int x; cin >> x; while (!st.empty ()&&st.top ()<=x){ st.pop (); cnt--; } ans+=cnt; st.push (x); cnt++; } } cout << ans; return 0 ; }
优先队列 https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/78306/E 大顶堆
单调队列 二维单调队列
框架 入 、出、记录答案
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1bM411X72E/?spm_id_from=333.337.search-card.all.click&vd_source=4452cbcad134fb17ec9cfb03a0acbdac
https://www.acwing.com/solution/content/97229/这个讲解很好
滑动窗口的框架
1.入
2.出
3.记录答案
题目 https://www.acwing.com/blog/content/29432/
用STL的双端队列deque非常方便
例题 洛谷P2032
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;const int N = 2e6 + 10 ;struct node {int v,id;}a[N];deque<node> q; int n,k;int main () cin >> n >>k; for (int i= 1 ; i <= n; i ++){ cin >> a[i].v; a[i].id = i; } for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i ++){ while (!q.empty ()&&q.back ().v<a[i].v){ q.pop_back (); } q.push_back (a[i]); if (q.front ().id==i-k)q.pop_front (); if (i>=k)cout << q.front ().v<<endl; } return 0 ; }
好消息,虽然抽象但是题型固定就那几个
https://www.acwing.com/solution/content/27437/ 这个非常易于适合理解单调栈
单调栈:见博客
单调队列:见博客https://blog.csdn.net/qq_50285142/article/details/120245122?ops_request_misc=%257B%2522request%255Fid%2522%253A%2522169761847116800180675961%2522%252C%2522scm%2522%253A%252220140713.130102334..%2522%257D&request_id=169761847116800180675961&biz_id=0&utm_medium=distribute.pc_search_result.none-task-blog-2~all~top_positive~default-1-120245122-null-null.142^v96^pc_search_result_base1&utm_term=%E5%8D%95%E8%B0%83%E9%98%9F%E5%88%97&spm=1018.2226.3001.4187
kmp算法(略) Trie 题一般字符串字母类型少
算法竞赛里的trie树最多26个或者52个字母
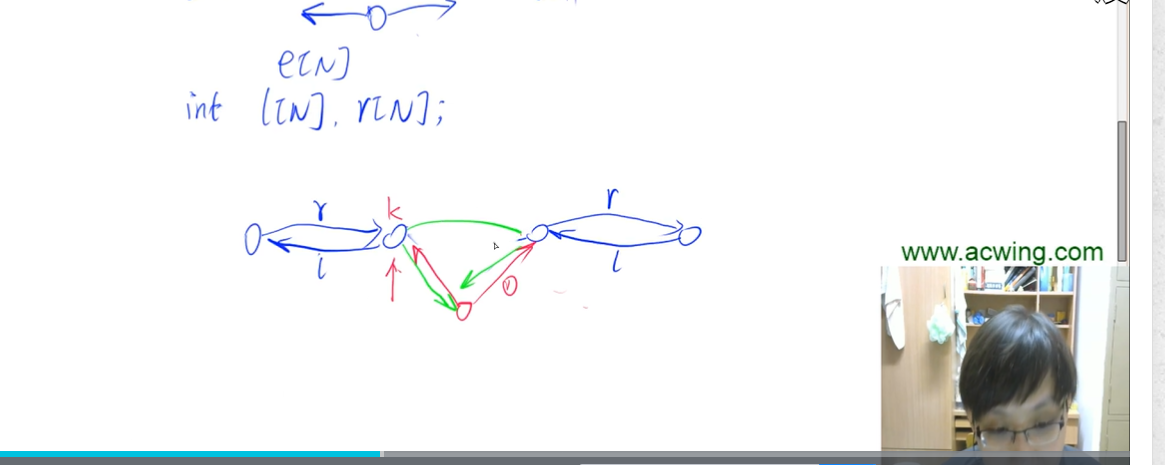
并查集 时间复杂度取决于树的深度
路径压缩使树的深度变小,提高查询效率O(1)
https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P1455 01背包+并查集
https://www.cnblogs.com/Eleven-Qian-Shan/p/13154721.html 很好的并查集博客
https://blog.csdn.net/hahalidaxin/article/details/51017473 一个不错的题解
https://www.luogu.com.cn/training/3065#problems 模板题
https://www.cnblogs.com/z-sm/p/12383918.html
https://leetcode.cn/circle/discuss/qmjuMW/
https://www.acwing.com/solution/content/33345/
https://www.acwing.com/activity/content/problem/content/886/ 模板题,记得合并前判断是否已经合并,不然size会加多
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/2068345
https://pintia.cn/problem-sets/994805342720868352/exam/problems/994805354108403712?type=7&page=1
#include <iostream> using namespace std;const int N=100010 ;int p[N];int find (int x) if (p[x]!=x) p[x]=find (p[x]); return p[x]; } int main () int n,m; scanf ("%d%d" ,&n,&m); for (int i=1 ;i<=n;i++) p[i]=i; while (m--) { char op[2 ]; int a,b; scanf ("%s%d%d" ,op,&a,&b); if (*op=='M' ) p[find (a)]=find (b); else if (find (a)==find (b)) printf ("Yes\n" ); else printf ("No\n" ); } return 0 ; }
https://www.cnblogs.com/zhxmdefj/p/11117791.html 并查集、带权并查集博客
堆 https://www.acwing.com/solution/content/3258/
#include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <queue> using namespace std;int main () int n; scanf ("%d" , &n); priority_queue<int , vector<int >, greater<int >> heap; while (n -- ){ int x; scanf ("%d" , &x); heap.push (x); } int res = 0 ;while (heap.size () > 1 ){ int a = heap.top (); heap.pop (); int b = heap.top (); heap.pop (); res += a + b; heap.push (a + b); } printf ("%d\n" , res);return 0 ;}
哈希 https://www.acwing.com/activity/content/problem/content/8034/ 感觉查找匹配还是哈希好写一些
https://www.acwing.com/activity/content/problem/content/8029/ 四平方和
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1SZ4y1z7wT/?spm_id_from=333.337.search-card.all.click&vd_source=4452cbcad134fb17ec9cfb03a0acbdac
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_51439643/article/details/122983920?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502 字符串哈希
树状数组 求逆序对 https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P1908
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1ce411u7qP/?spm_id_from=333.337.search-card.all.click&vd_source=4452cbcad134fb17ec9cfb03a0acbdac
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV14r421W7oR/?spm_id_from=333.337.search-card.all.click&vd_source=4452cbcad134fb17ec9cfb03a0acbdac 原理讲得好 根据二进制位从右往左拆分
查询 更新 都是 O(logN)
例题 动态求区间和 树状数组 模板1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;const int N=100009 ;int a[N],tr[N];int n,m;int lowbit (int x) return x&-x; } int add (int x,int v) for (int i=x;i<=n;i+=lowbit (i)) tr[i]+=v; } int qurry (int x) int cnt=0 ; for (int i=x;i!=0 ;i-=lowbit (i)){ cnt+=tr[i]; } return cnt; } int main () cin>>n>>m; for (int i=1 ;i<=n;i++) scanf ("%d" ,&a[i]); for (int i=1 ;i<=n;i++) add (i,a[i]); while (m--){ int k,x,y; scanf ("%d%d%d" ,&k,&x,&y); if (k==0 ) printf ("%d\n" ,qurry (y)-qurry (x-1 )); else add (x,y); } return 0 ;}
树状数组 模板2
https://www.luogu.com.cn/article/g7ci886q
区间修改、区间查询: https://blog.csdn.net/Wu_while/article/details/119491559
[同时支持区间修改、区间查询](
3.第三章 搜索与图论 DFS和BFS区别 https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-level-order-traversal/solutions/244853/bfs-de-shi-yong-chang-jing-zong-jie-ceng-xu-bian-l/
递归 https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1UD4y1Y769/?spm_id_from=333.880.my_history.page.click&vd_source=4452cbcad134fb17ec9cfb03a0acbdac
https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-depth-of-binary-tree/solutions/2010612/kan-wan-zhe-ge-shi-pin-rang-ni-dui-di-gu-44uz/ 二叉树最大深度
https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-depth-of-binary-tree/submissions/511924007/ 二叉树最小深度,要考虑全面 (好题)
https://leetcode.cn/problems/path-sum/description/ 路径总和I (AC)
https://leetcode.cn/problems/path-sum-ii/description/ 路径总和II (AC)
https://leetcode.cn/problems/sum-root-to-leaf-numbers/ 求根节点到叶节点之和(AC)
https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-paths/description/ 好题 二叉树的所有路径
https://leetcode.cn/problems/vertical-order-traversal-of-a-binary-tree/ 二叉树垂序遍历(未做)
https://leetcode.cn/problems/same-tree/ 相同的树
https://leetcode.cn/problems/symmetric-tree/ 对称二叉树
https://leetcode.cn/problems/balanced-binary-tree/solutions/2015068/ru-he-ling-huo-yun-yong-di-gui-lai-kan-s-c3wj/ 平衡二叉树
https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-right-side-view/solutions/2015061/ru-he-ling-huo-yun-yong-di-gui-lai-kan-s-r1nc/ 二叉树的右视图
https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-right-side-view/ 二叉树的右视图 , BFS DFS都可以用
https://leetcode.cn/problems/invert-binary-tree/solutions/791028/yi-pian-wen-zhang-dai-ni-chi-tou-dui-che-21l9/ 对称性递归
https://leetcode.cn/problems/invert-binary-tree/solutions/73159/dong-hua-yan-shi-liang-chong-shi-xian-226-fan-zhua/ 好题 后序遍历
节点与其祖先之间的最大差值 好题
换个角度看问题:对于一条从根出发向下的路径,我们要计算的实际上是这条路径上任意两点的最大差值。
递归到叶子时,mx\textit{mx}mx 是从根到叶子的路径上的最大值,mn\textit{mn}mn 是从根到叶子的路径上的最小值,所以 mx−mn\textit{mx}-\textit{mn}mx−mn 就是从根到叶子的路径上任意两点的最大差值。
所以无需每个节点都去更新答案,而是在递归到终点时才去更新答案。
作者:灵茶山艾府https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-difference-between-node-and-ancestor/solutions/2232367/liang-chong-fang-fa-zi-ding-xiang-xia-zi-wj9v/
根到叶路径上的不足节点
https://leetcode.cn/problems/insufficient-nodes-in-root-to-leaf-paths/solutions/2277376/python3-di-gui-xiang-jie-1080-gen-dao-xi-cc4a/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/validate-binary-search-tree/ 验证二叉搜索树
https://leetcode.cn/problems/search-in-a-binary-search-tree/description/ 二叉搜索树中的搜索
https://leetcode.cn/problems/range-sum-of-bst/description/ 二叉搜索树的范围和
https://leetcode.cn/problems/insufficient-nodes-in-root-to-leaf-paths/submissions/512285467/ gpt生成的该题题解
删点成林 https://leetcode.cn/problems/delete-nodes-and-return-forest/ 未做
二叉树中的最长交错路径 https://leetcode.cn/problems/longest-zigzag-path-in-a-binary-tree/ 未做
https://leetcode.cn/problems/diameter-of-binary-tree/solutions/2227017/shi-pin-che-di-zhang-wo-zhi-jing-dpcong-taqma/ 树形DP
二叉树的直径 https://leetcode.cn/problems/diameter-of-binary-tree/solution/shi-pin-che-di-zhang-wo-zhi-jing-dpcong-taqma/
二叉树中的最大路径和 https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-maximum-path-sum/solution/shi-pin-che-di-zhang-wo-zhi-jing-dpcong-n9s91/ (反复调试AC,灵神题解很优美)
https://www.acwing.com/activity/content/problem/content/9764/ 蓝桥杯 大臣的旅费 树的直径,树形DP
https://www.acwing.com/activity/content/problem/content/9767/ 木棒 每日一题
https://www.acwing.com/activity/content/problem/content/9769/ 糖果
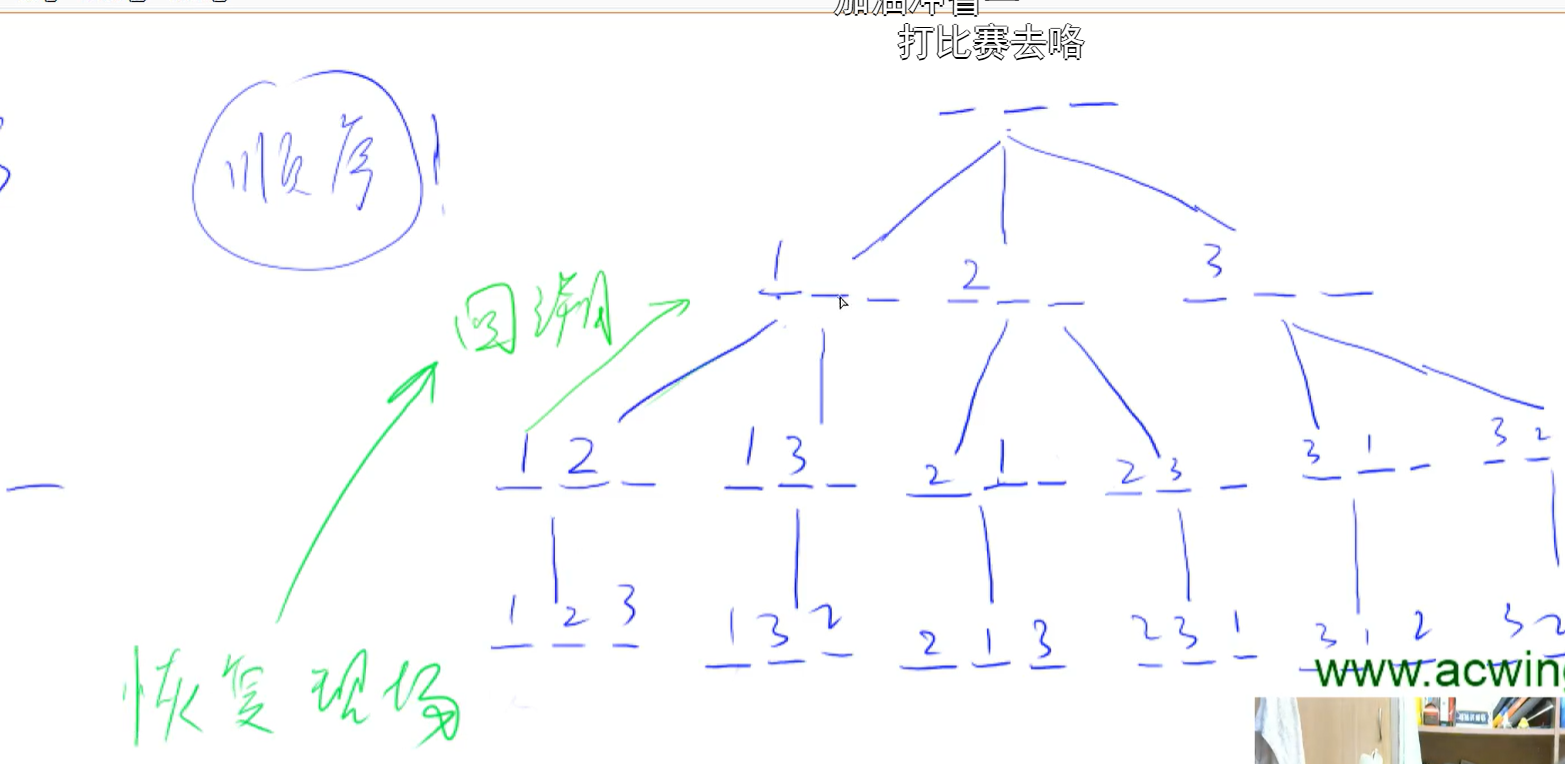
回溯 https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P8642 洛谷绿题
子集
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1mG4y1A7Gu/?spm_id_from=333.880.my_history.page.click&vd_source=4452cbcad134fb17ec9cfb03a0acbdac
https://leetcode.cn/problems/palindrome-partitioning/description/ 分割回文串(灵神代码优美)
https://leetcode.cn/problems/letter-case-permutation/ 字母大小写全排列
组合
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1xG4y1F7nC/?spm_id_from=333.788&vd_source=4452cbcad134fb17ec9cfb03a0acbdac
https://leetcode.cn/problems/combination-sum-iii/description/ 组合总和III
https://leetcode.cn/problems/generate-parentheses/ 括号生成
https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/76133/E 牛客周赛例题
情况1:两个点最短路相同,连一起最短路仍然不变,可以加边
情况2:两个最短路的绝对值差为1
无解的情况
1、[0,1,2,4,4,5,6]:没有3
2、m<n-1 点<边的数量
第一次构造 第一种情况
第二次构造 第二种情况
#include <bits/stdc++.h> #define int long long using namespace std;int n, m;const int mod = 1e9 + 7 ;signed main () cin >> n >> m; if (m < n - 1 ){ cout << -1 << endl; return 0 ; } vector<int > g[n + 10 ]; vector<int > a (n + 1 ) ; int ma = -1 ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i ++){ cin >> a[i]; ma = max (ma, a[i]); g[a[i]].push_back (i); } vector<pair<int , int >> ans; for (int i = 1 ; i <= ma; i ++){ if (g[i - 1 ].empty ()){ cout << "-1" ; return 0 ; } } for (int i = 1 ; i <= ma; i ++){ for (auto k: g[i]){ ans.push_back ({g[i - 1 ][0 ], k}); } } for (int i = 1 ; i <= ma; i ++){ for (int j = 1 ; j < g[i].size (); j ++){ for (int k = j - 1 ; k >= 0 ; k --){ ans.push_back ({g[i][j], g[i][k]}); if (ans.size () == m)break ; } if (ans.size () == m) break ; } if (ans.size () == m) break ; } for (int i = 1 ; i <= ma; i ++){ for (int j = 1 ; j < g[i - 1 ].size (); j ++){ for (int k = 1 ; k < g[i].size (); k ++){ ans.push_back ({g[i - 1 ][j],g[i][k]}); if (ans.size ()==m)break ; } if (ans.size () == m)break ; } if (ans.size () == m)break ; } if (ans.size () < m){ cout << -1 ; }else { for (auto i : ans){ cout<<i.first <<" " <<i.second << endl; } } return 0 ; }
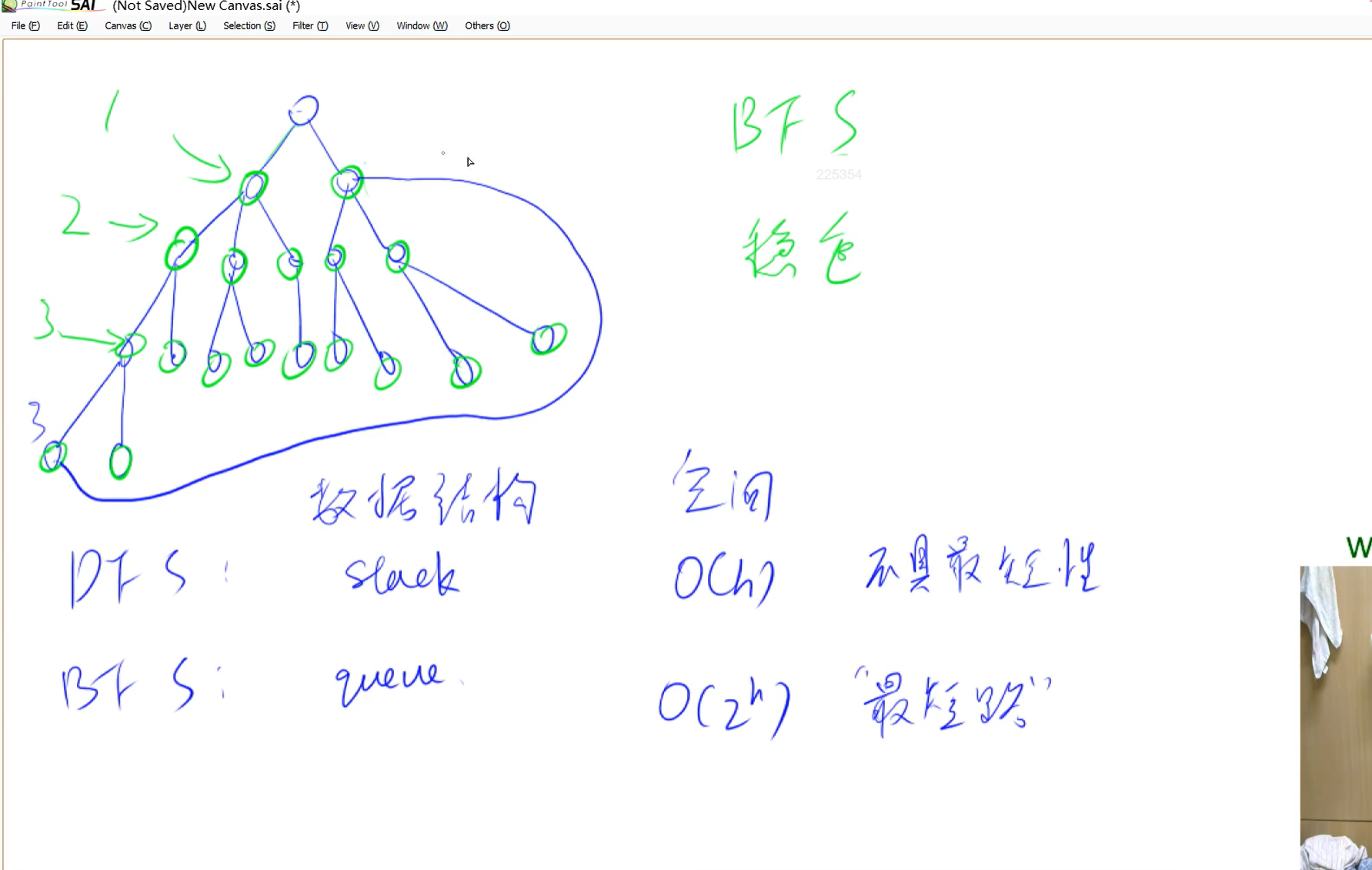
深度优先搜索(DFS)
两个很重要的概念:回溯 剪枝
每个DFS都一定对应一个搜索树
https://www.acwing.com/solution/content/30988/
https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/solution/P5194 求最大值 从后往前
https://www.cnblogs.com/lcez56jsy/p/10705834.html 迷宫 求方案数
https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P1101 单词方阵(搜一个字符串)
#include <cstdio> #include <iostream> #include <cstring> using namespace std;const int maxn = 110 ;const int dx[] = {1 , 1 , 1 , 0 , 0 , -1 ,-1 ,-1 }; const int dy[] = {1 , 0 ,-1 , 1 ,-1 , 0 , 1 ,-1 };const string cmp = "yizhong" ; char A[maxn][maxn], ans[maxn][maxn];int mark[maxn][maxn], n;void dfs (int x,int y) for (int i = 0 ;i < 8 ;i++) { int flag = 1 ; for (int j = 1 ;j <= 6 ;j++) { int nx = x + j*dx[i]; int ny = y + j*dy[i]; if (nx < 1 || nx > n || ny < 1 || ny > n) { flag = 0 ; break ; } if (cmp[j] != A[nx][ny]) { flag = 0 ; break ; } } if (flag == 0 ) continue ; for (int j = 0 ;j <= 6 ;j++) { int nx = x + j*dx[i]; int ny = y + j*dy[i]; ans[nx][ny] = A[nx][ny]; } } return ; } int main () cin >> n; for (int i = 1 ;i <= n;i++) { for (int j = 1 ;j <= n;j++) { cin >> A[i][j]; } } for (int i = 1 ;i <= n;i++) { for (int j = 1 ;j <= n;j++) { if (A[i][j] == 'y' ) dfs (i,j); } } for (int i = 1 ;i <= n;i++) { for (int j = 1 ;j <= n;j++) { if (ans[i][j] == 0 ) ans[i][j] = '*' ; cout << ans[i][j]; } cout << endl; } return 0 ; }
https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P1019 单词接龙https://www.cnblogs.com/dx123/p/17486562.html
最后ans - 1是因为有前面的*,前面加 * 可以方便j从1开始枚举,不用特判
经典题目 八皇后
广度优先搜索(BFS) 迷宫问题 https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1176807把DFS和BFS区别讲的很明白
2019蓝桥 https://blog.csdn.net/m0_56312312/article/details/123671856 思路很好,字典序数组按照顺序排好了,第一个得到的路径必然是最短的并且字典序最小的
https://www.luogu.com.cn/paste/sa0zary9 题单
例题 蓝桥国赛 迷宫与陷阱 :https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P8673
例题 全球变暖 https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/description/1235/
注意 迷宫(这题不建议用bfs) https://www.cnblogs.com/lcez56jsy/p/10705834.html 和DFS的区别(回溯)
Flood fill(洪水灌溉)
1.多少个连通块
不是所有最短路都用BFS,只能当边权都是1时,一般情况都是用最短路算法
BFS函数里一般都用队列
2.多少个被淹没
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;typedef pair<int , int > PII;const int N = 1e3 + 10 ;int n;char g[N][N];bool vis[N][N];int judge[N][N];int cnt;queue<PII> q; int dx[5 ] = {0 ,0 ,1 ,0 ,-1 },dy[5 ] = {0 ,1 ,0 ,-1 ,0 };void BFS1 (int x,int y) while (!q.empty ()){ auto t = q.front (); q.pop (); for (int i = 0 ; i < 5 ;i ++){ int x = dx[i] + t.first, y = dy[i] +t.second; if (x>=1 &&x<=n&&y>=1 &&y<=n&&vis[x][y]==false &&g[x][y]=='#' &&(g[x-1 ][y]=='.' ||g[x+1 ][y]=='.' ||g[x][y-1 ]=='.' ||g[x][y+1 ]=='.' )){ vis[x][y] = true ; judge[x][y]= 1 ; q.push ({x,y}); } } } } void BFS2 (int x,int y) int flag = 0 ; while (!q.empty ()){ auto t = q.front (); q.pop (); for (int i = 0 ; i < 5 ; i ++){ int x= dx[i] +t.first,y=dy[i]+t.second; if (x>=1 &&x<=n&&y>=1 &&y<=n&&g[x][y]=='#' &&vis[x][y]==false ){ vis[x][y] = true ; if (judge[x][y]==0 ){ flag = 1 ; } q.push ({x,y}); } } } if (flag == 0 )cnt++; } int main () cin >> n; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i ++){ for (int j = 1 ; j <= n; j ++){ cin >> g[i][j]; } } for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i ++){ for (int j = 1 ; j <= n; j ++){ if (g[i][j] == '#' &&vis[i][j]==false ){ q.push ({i,j}); BFS1 (i,j); } } } memset (vis,false ,sizeof vis); for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i ++){ for (int j = 1 ; j <= n; j ++){ if (g[i][j] == '#' &&vis[i][j]==false ){ q.push ({i,j}); BFS2 (i,j); } } } cout << cnt; return 0 ; }
岛屿个数 https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/description/4962/
两个BFS,特别好的题,注意海水渗透要8个方向。
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;typedef pair<int , int > PII;const int N = 55 ;int T;char g[N][N];queue<PII> q; int n,m;int dx[8 ] = {1 ,0 ,-1 ,0 , 1 , 1 ,-1 , - 1 };int dy[8 ] = {0 ,1 ,0 ,-1 ,-1 ,1 ,-1 ,1 };void BFS1 () q.push ({0 ,0 }); g[0 ][0 ] = '2' ; while (!q.empty ()){ auto t = q.front (); q.pop (); for (int i = 0 ;i < 8 ; i ++){ int x = t.first + dx[i], y = t.second + dy[i]; if (x >= 0 && x<=n+1 && y >=0 && y <=m + 1 && g[x][y]=='0' ){ g[x][y] = '2' ; q.push ({x,y}); } } } } void BFS2 (int x, int y) q.push ({x,y}); g[x][y] = '2' ; while (!q.empty ()){ auto t = q.front (); q.pop (); for (int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i ++){ int x = t.first + dx[i], y = t.second + dy[i]; if (x >= 1 && x <= n && y>=1 &&y <=m && (g[x][y]=='0' ||g[x][y]=='1' )){ g[x][y] = '2' ; q.push ({x,y}); } } } } int main () cin >> T; while (T --){ memset (g,'0' ,sizeof g); cin >> n >> m; int ans = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i ++){ for (int j = 1 ; j <= m; j ++){ cin >> g[i][j]; } } BFS1 (); for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i ++){ for (int j =1 ; j <= m; j ++){ if (g[i][j] == '1' ){ BFS2 (i, j); ans ++; } } } cout << ans << endl; } }
树与图的存储(10.21)
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1mJ411S7BB/?spm_id_from=333.337.search-card.all.click&vd_source=4452cbcad134fb17ec9cfb03a0acbdac
这个链式前向星讲的特别好↑
树是特殊的图,所以只讲图就行
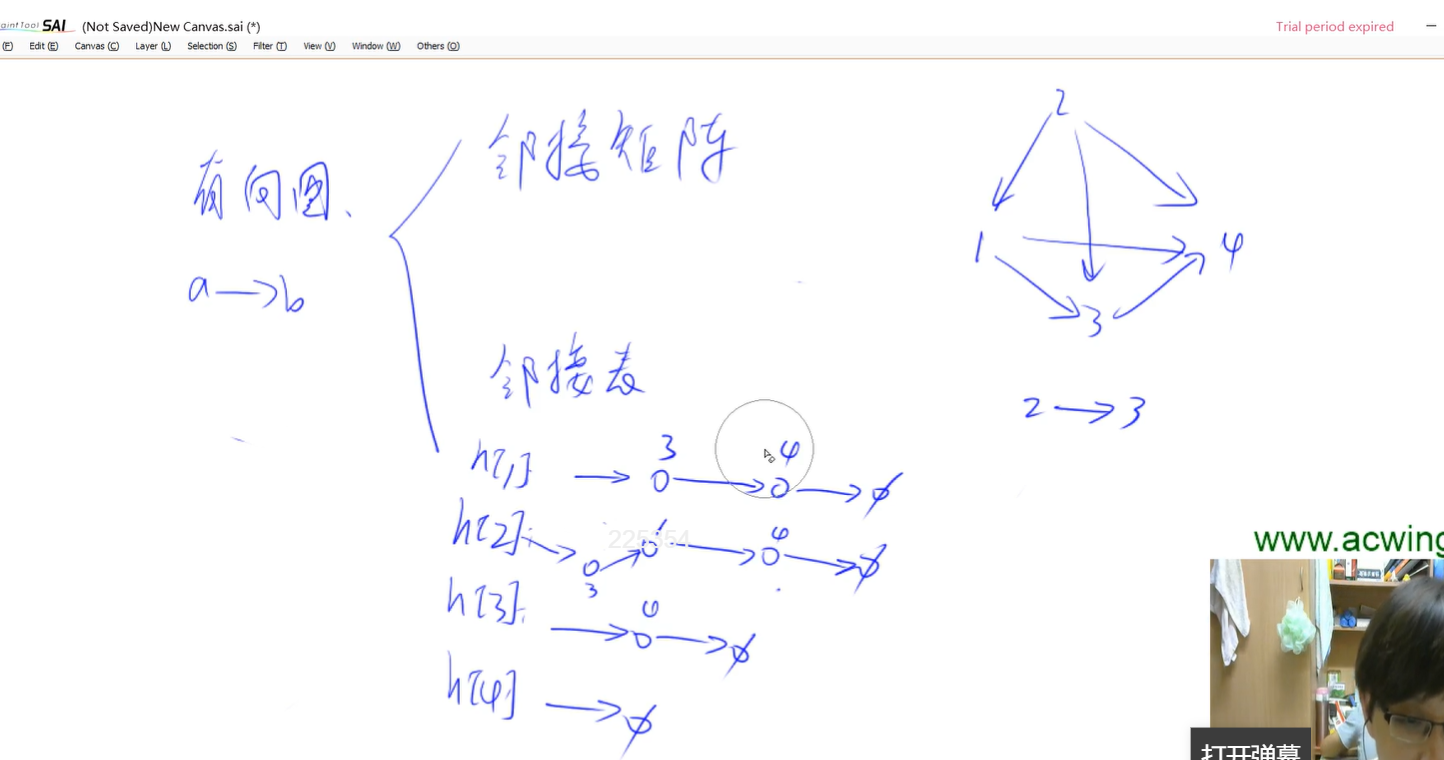
图:有向图,无向图,边有无方向,无向图可以看作特殊的有向图,所以只要看有向图
有向图(a->b):
邻接矩阵g[a] [b] a->b,有重边保留一条就可以了
邻接表
树与图的深度优先遍历
**https://leetcode.cn/circle/discuss/FyPTTM/**宝藏
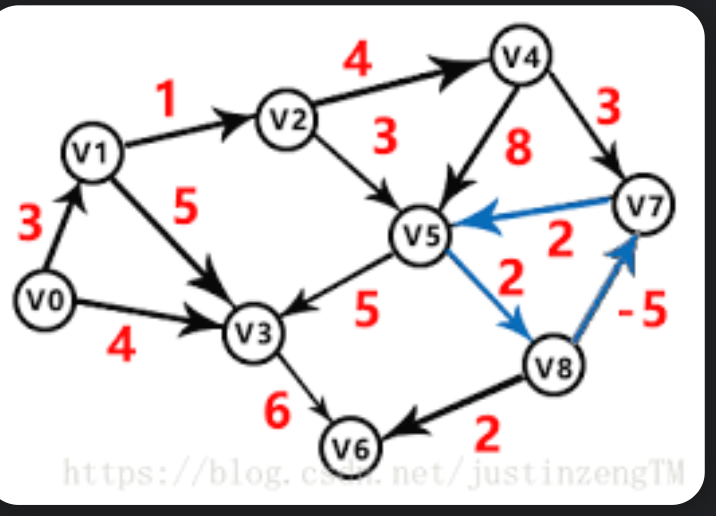
讲解了为什么要反向建边 https://www.163.com/dy/article/E01JK0430538071X.html
https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P3916
洛谷这个题↑正向遍历超时了 n 1e5 ,用反向遍历更适合
思路真妙,把大的先走完,打上标记,肯定就是最大的了
图的讲解 (2023.12.4很好) https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/solution/P5318
这个邻接表写法 nice↓
#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <queue> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> using namespace std;const int MAXN = 100010 ;std::vector<int > G[MAXN]; int n, m;bool visited[MAXN];queue<int > q; void dfs (int x, int cur) visited[x] = true ; cout << x << " " ; if (cur == n) return ; for (int i=0 ; i<G[x].size (); i++) if (!visited[G[x][i]]) dfs (G[x][i], cur+1 ); } void bfs (int x) memset (visited, false , sizeof (visited)); visited[x] = true ; q.push (x); while (!q.empty ()) { int v = q.front (); q.pop (); cout << v << " " ; for (int i=0 ; i<G[v].size (); i++) if (!visited[G[v][i]]) { visited[G[v][i]] = true ; q.push (G[v][i]); } } } int main () cin >> n >> m; for (int i=1 ; i<=m; i++) { int u, v; cin >> u >> v; G[u].push_back (v); } for (int i=1 ; i<=n; i++) sort (G[i].begin (), G[i].end ()); dfs (1 , 0 ); cout << endl; bfs (1 ); cout << endl; return 0 ; }
非常重要 !!!由前+中/后+中构建序列 模板(字符串切割 + 练习STL substr)
https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/solution/P1827
由中序和前序求后序 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;string pre,inor; void dfs (string pre,string inor) if (pre.empty ())return ; char root = pre[0 ]; int k = inor.find (root); pre.erase (pre.begin ()); string leftpre = pre.substr (0 ,k); string rightpre = pre.substr (k); string leftinor = inor.substr (0 ,k); string rightinor = inor.substr (k + 1 ); dfs (leftpre,leftinor); dfs (rightpre,rightinor); printf ("%c" ,root); } int main () cin >> inor >>pre ; dfs (pre,inor); putchar ('\n' ); return 0 ; }
https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P1030
由中序和后序求前序 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;string inor,post; void solve (string inor,string post) if (post.empty ())return ; char root = post[post.size () - 1 ]; post.erase (post.end ()-1 ); int k = inor.find (root); string inorleft = inor.substr (0 ,k); string inorright= inor.substr (k + 1 ); string postleft = post.substr (0 ,k); string postright = post.substr (k); cout << root; solve (inorleft,postleft); solve (inorright,postright); } int main () cin >> inor >> post; solve (inor,post); return 0 ; }
#include <string> #include <cstring> #include <iostream> #include <cstdio> using namespace std;string pre,inor; void work (string pre,string inor) if (pre.empty ())return ; char root=pre[0 ]; int k=inor.find (root); pre.erase (pre.begin ()); string leftpre=pre.substr (0 ,k); string rightpre=pre.substr (k); string leftinor=inor.substr (0 ,k); string rightinor=inor.substr (k+1 ); work (leftpre,leftinor); work (rightpre,rightinor); printf ("%c" ,root); } int main () cin>>inor>>pre; work (pre,inor); putchar ('\n' ); return 0 ; }
树与图的宽度优先遍历(待更) DAG() 与 拓扑排序(12.4) 知乎的讲解 ,很好↓[知识点]
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/135094687
拓扑排序邻接表版 [代码]
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/850/
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;const int N = 1e5 + 10 ;vector<int > G[N]; queue<int > q; int d[N];int n,m,cnt,ans[N];int main () cin >> n >> m; for (int i = 1 ;i <= m; i ++){ int x,y; cin >> x>> y; G[x].push_back (y); d[y]++; } for (int i =1 ; i <= n; i ++){ if (d[i]==0 )q.push (i); } while (q.size ()){ int t = q.front (); q.pop (); ans[cnt++] = t; for (int i = 0 ; i < G[t].size ();i ++){ d[G[t][i]]--; if (d[G[t][i]]==0 ) q.push (G[t][i]); } } if (cnt == n)for (int i = 0 ; i <cnt; i ++)cout << ans[i]<<" " ; else cout <<-1 ; return 0 ; }
例题
我发现下面两道需要拓扑的题,只需要把一些求ans的代码放到模板里,模板还是不变的
1 .洛谷P1113 杂务
#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <queue> using namespace std;const int N = 500005 ;int ind[N], f[N], a[N]; vector<int > edge[N]; queue<int > q; int main () int n; cin >> n; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { int x; cin >> x; cin >> a[i]; while (true ) { int y; cin >> y; if (y == 0 ) break ; edge[y].push_back (x); ind[x]++; } } for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { if (ind[i] == 0 ) { q.push (i); f[i] = a[i]; } }; while (!q.empty ()) { int rhs = q.front (); q.pop (); for (int i = 0 ; i < edge[rhs].size (); i++) { int u = edge[rhs][i]; ind[u]--; if (ind[u] == 0 ) q.push (u); f[u] = max (f[u], f[rhs] + a[u]); } } int ans = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { ans = max (ans, f[i]); } cout << ans << endl; return 0 ; }
2.P4017 最大食物链计数
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;const int N = 5e3 + 10 ;int ans[N],outd[N],ind[N];vector<int >G[N]; queue<int >q; int main () int n,m; cin >> n >> m; for (int i = 0 ; i < m; i ++){ int x,y; cin >> x >> y; ind[y]++; outd[x]++; G[x].push_back (y); } for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i ++){ if (ind[i]==0 ){ q.push (i); ans[i] = 1 ; } } while (q.size ()){ auto t = q.front (); q.pop (); for (int i = 0 ; i < G[t].size (); i ++){ int x = G[t][i]; ind[x] --; if (ind[x]==0 ){ q.push (x); } ans[x] = (ans[x] + ans[t])%80112002 ; } } int res = 0 ;for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i ++){ if (outd[i]==0 ){ res= (res + ans[i])%80112002 ; } } cout << res; return 0 ;}
最短路径 力扣总结精华 https://leetcode.cn/circle/discuss/FyPTTM/#%E6%9C%80%E7%9F%AD%E8%B7%AF%E5%BE%84
有权单源最短路
无权单源最短路
带权全源最短路
如果是无权单源,可以BFS+队列,有权就不行了
带权单源最短路 Dijkstra
视频演示 :
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1zz4y1m7Nq/?spm_id_from=333.788.recommend_more_video.0&vd_source=4452cbcad134fb17ec9cfb03a0acbdac
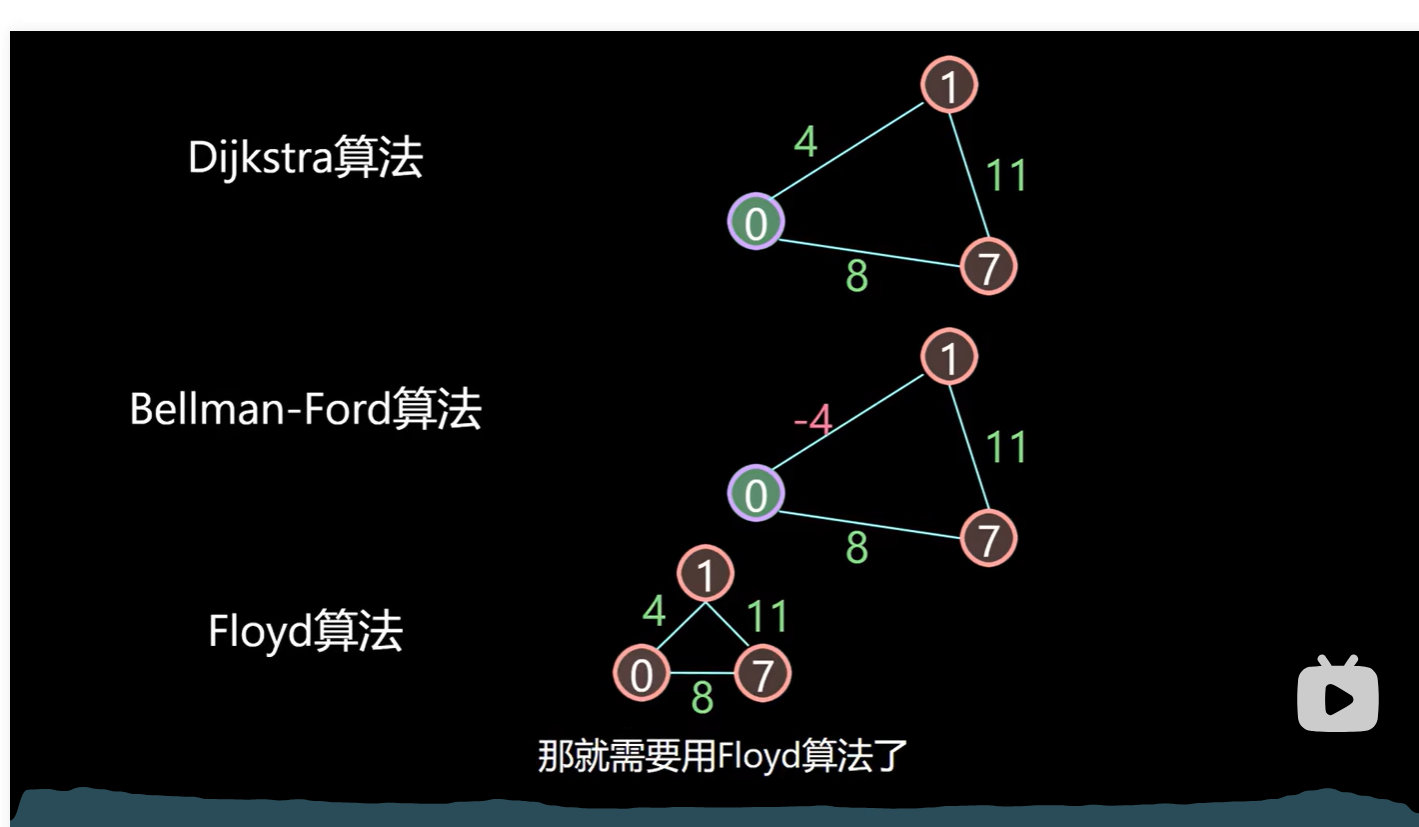
各个算法用途比较
https://www.acwing.com/solution/content/5806/ 代码详解
朴素版 #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <cstring> using namespace std;const int N=510 ;int g[N][N]; int dist[N]; bool st[N]; int n,m;int Dijkstra () memset (dist, 0x3f ,sizeof dist); dist[1 ]=0 ; for (int i=0 ;i<n;i++) { int t=-1 ; for (int j=1 ;j<=n;j++) if (!st[j]&&(t==-1 ||dist[j]<dist[t])) t=j; st[t]=true ; for (int j=1 ;j<=n;j++) dist[j]=min (dist[j],dist[t]+g[t][j]); } if (dist[n]==0x3f3f3f3f ) return -1 ; return dist[n];} int main () cin>>n>>m; memset (g,0x3f ,sizeof g); while (m--){ int x,y,z; cin>>x>>y>>z; g[x][y]=min (g[x][y],z); } cout<<Dijkstra ()<<endl; return 0 ;}
对于「稠密图」,应当使用「朴素版」,对于「稀疏图」,应当使用「优先队列版」
堆优化版 (vector邻接表,但是大多用的还是数组模拟邻接表)
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;typedef pair<int ,int >PII;const int N = 1e5 + 10 ;vector<PII>G[N]; int dist[N];bool st[N];int n,m;int dijkstra () memset (dist,0x3f ,sizeof dist); dist[1 ] = 0 ; priority_queue<PII,vector<PII>,greater<PII>>heap; heap.push ({0 ,1 }); while (heap.size ()){ auto t = heap.top (); heap.pop (); int distance = t.first,node = t.second; if (st[node])continue ; st[node] = true ; for (int i = 0 ; i < G[node].size (); i ++){ int newNode = G[node][i].first; int len = G[node][i].second; if (dist[newNode]>dist[node] + len){ dist[newNode] = dist[node] + len; heap.push ({dist[newNode],newNode}); } } } if (dist[n] == 0x3f3f3f3f )return -1 ; else return dist[n]; } int main () cin >> n >> m; G.resize (n + 1 ); for (int i = 0 ; i < m; i ++){ int x,y,z; cin >> x >> y >> z; G[x].push_back ({y,z}); } cout << dijkstra (); return 0 ; }
最短路径 和 各种第二标量 例题PTA甲级 紧急事件
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;int G[510 ][510 ];int dist[510 ];int num[510 ];int n,m,c1,c2;bool vis[510 ];int weight[510 ];int num2[510 ];void dijkstra () memset (dist,0x3f ,sizeof dist); dist[c1] = 0 ; num2[c1] = 1 ; num[c1] = weight[c1]; for (int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++){ int t = -1 ; for (int j = 0 ; j < n; j ++){ if (vis[j]==false &&(t==-1 ||dist[t] >dist[j])){ t = j; } } vis[t] = true ; for (int j = 0 ; j < n; j ++){ if (dist[t] + G[t][j] < dist[j]){ dist[j] = dist[t] + G[t][j]; num[j] = num[t] + weight[j]; num2[j] = num2[t]; }else if (dist[t] +G[t][j] == dist[j]){ num2[j] += num2[t]; if (weight[j] + num[t] > num[j]) num[j] = num[t] + weight[j]; } } } cout << num2[c2] <<" " <<num[c2]; } int main () cin >>n >> m >>c1>>c2; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i ++){ cin >> weight[i]; } memset (G,0x3f ,sizeof G); while (m --){ int x,y,z; cin >> x >> y >> z; G[x][y] = min (G[x][y],z); G[y][x] = min (G[y][x],z); } dijkstra (); return 0 ; }
书P375
打印路径 void DFS (int s,int v) if (v == s){ printf ("%d\n" ,s); return ; } DFS (s,pre[v]); printf ("%d\n" ,v); }
为什么无法处理负边
https://www.acwing.com/solution/content/6320/详解很好
bellman-ford 与spfa比可能唯一的好处:如果是有边数限制的话,就不能用spfa了
时间复杂度 N*M
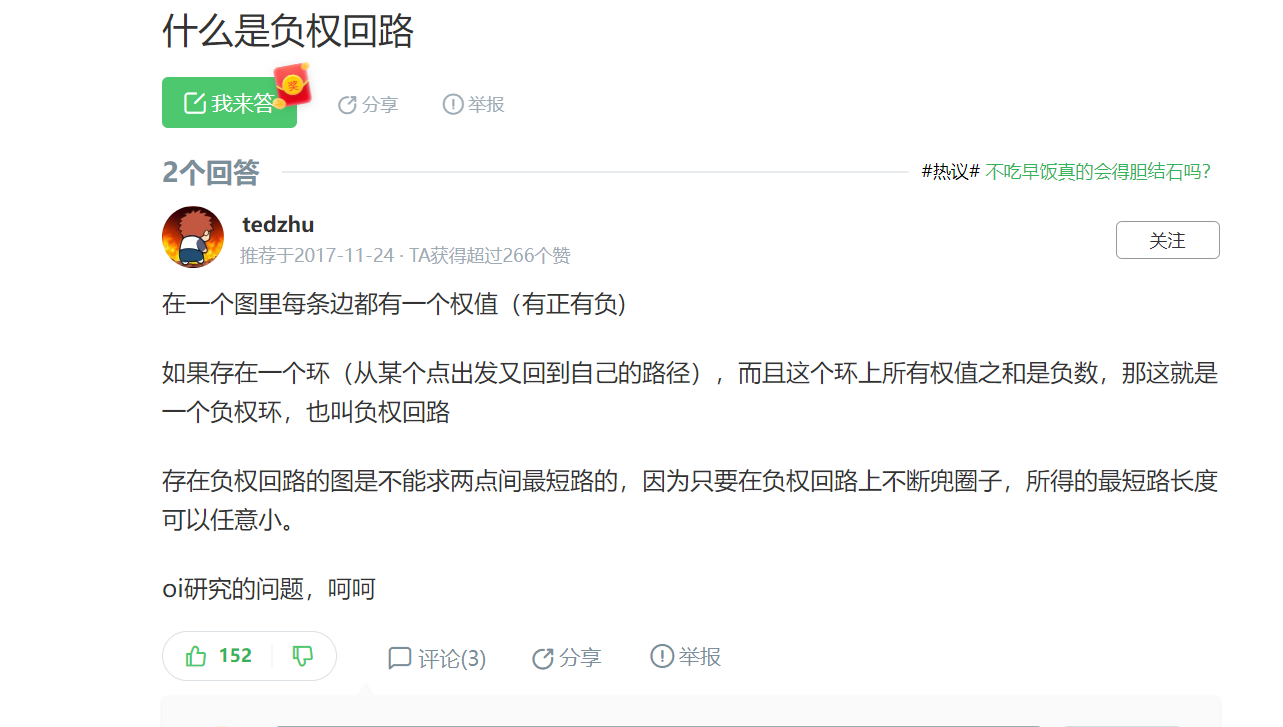
如果有负权回路的话,最短路不一定存在了
bellman-ford是可以求出是否有负环的,但平时不用,时间复杂度太高,后面SPFA会用到
鸽巢(抽屉)原理
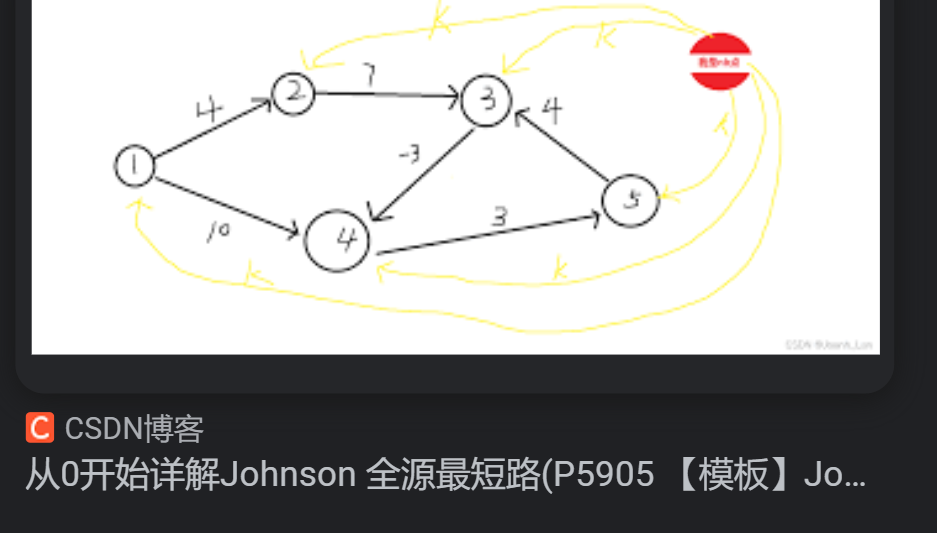
Spfa 多源汇最短路 Floyd 4.第四章 数学知识(12.10) 进制转换 (要很熟练)
转换成10进制用的秦九韶算法,迭代方式提升效率
位运算 洛谷 P1469 找筷子
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;int ans,n,a;int main () cin>>n; for (int i=1 ;i<=n;i++) { scanf ("%d" ,&a); ans^=a; } printf ("%d" ,ans); return 0 ; }
加法原理与乘法原理 结果可能很大,要对指定数字取余数。不能全部乘完之后再取余数,因为中间结果可能会溢出。可以乘完一次就取一次余数。实际上,加法或者乘法都可以这样做:
(a+b+c)%k = ((a+b)%k + c)%k
(a * b * c) % k = ((ab)%k * c )%k
组合数问题 例题
洛谷 P2822 [NOIP2016 提高组] 组合数问题
| 同余定理,前面是除数,后面是被除数
杨辉三角的性质
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;long long c[2010 ][2010 ];int main () int t,k,m,n; cin >> t >> k; for (int i = 0 ; i <= 2000 ; i ++){ c[i][0 ] = c[i][i] = 1 ; for (int j= 1 ; j < i ; j ++) c[i][j] = (c[i-1 ][j] + c[i-1 ][j-1 ])%k; } while (t--){ int ans = 0 ; cin >> n >> m; for (int i = 0 ; i <= n; i ++) for (int j = 0 ; j <= min (i,m); j ++) ans+=c[i][j] == 0 ; cout << ans << endl; } return 0 ; }
约数
例题 P2926 [USACO08DEC] Patting Heads S
未解决
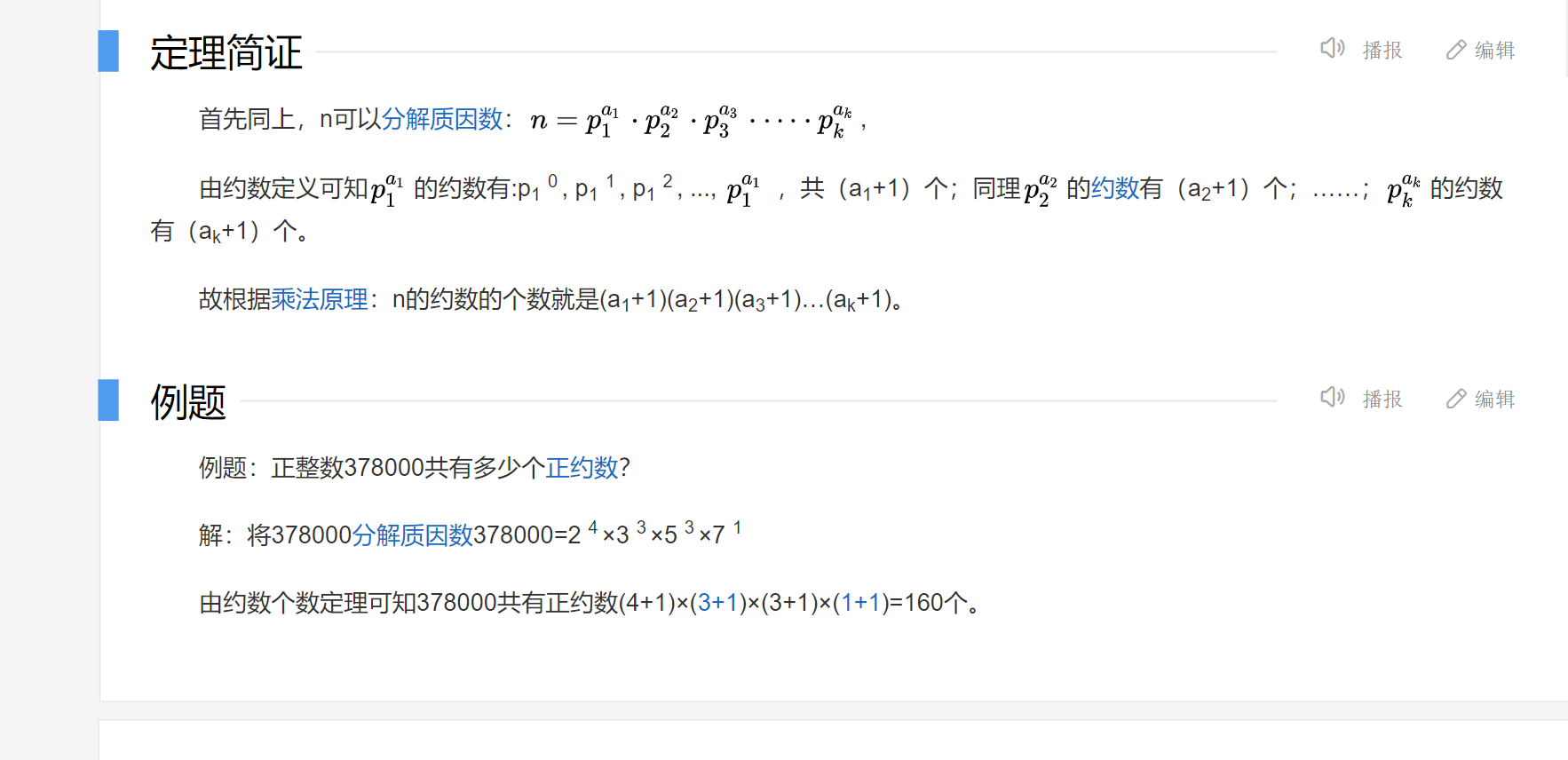
试除法求约数 约数个数和约数之和(两个公式) 约数个数证明:
质数和合数 所以,在以后的算法学习中,大家可以有意识地去使用线性筛进行解题,防止白给。除了这两种筛素数的方法,其实还有更加优秀的,时间复杂度低于O(N)的筛法,这里本人能力有限,就不进行介绍了,有兴趣的同学可以自己去查找相关资料。
埃氏筛 void get_primes1 () for (int i=2 ;i<=n;i++){ if (!st[i]){ primes[cnt++]=i; for (int j=i;j<=n;j+=i) st[j]=true ; } } }
线性筛 #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> using namespace std;const int N = 1000010 ;int primes[N], cnt;bool st[N];void get_primes (int n) for (int i = 2 ; i <= n; i++) { if (!st[i]) primes[cnt++] = i; for (int j = 0 ; primes[j] <= n / i; j ++) { st[primes[j]*i] = true ; if (i % primes[j] == 0 ) break ; } } } int main () int n; cin >> n; get_primes (n); cout << cnt << endl; return 0 ; }
分解质因数 https://www.acwing.com/solution/content/9813/
#include <iostream> #include <algorithm> using namespace std;int main (void ) int n;cin>>n; while (n--) { int a;cin>>a; for (int i=2 ;i<=a/i;i++) { if (a%i==0 ) { int s=0 ; while (a%i==0 ) { a/=i; s++; } cout<<i<<" " <<s<<endl; } } if (a>1 ) cout<<a<<' ' <<1 <<endl; cout<<endl; } return 0 ; }
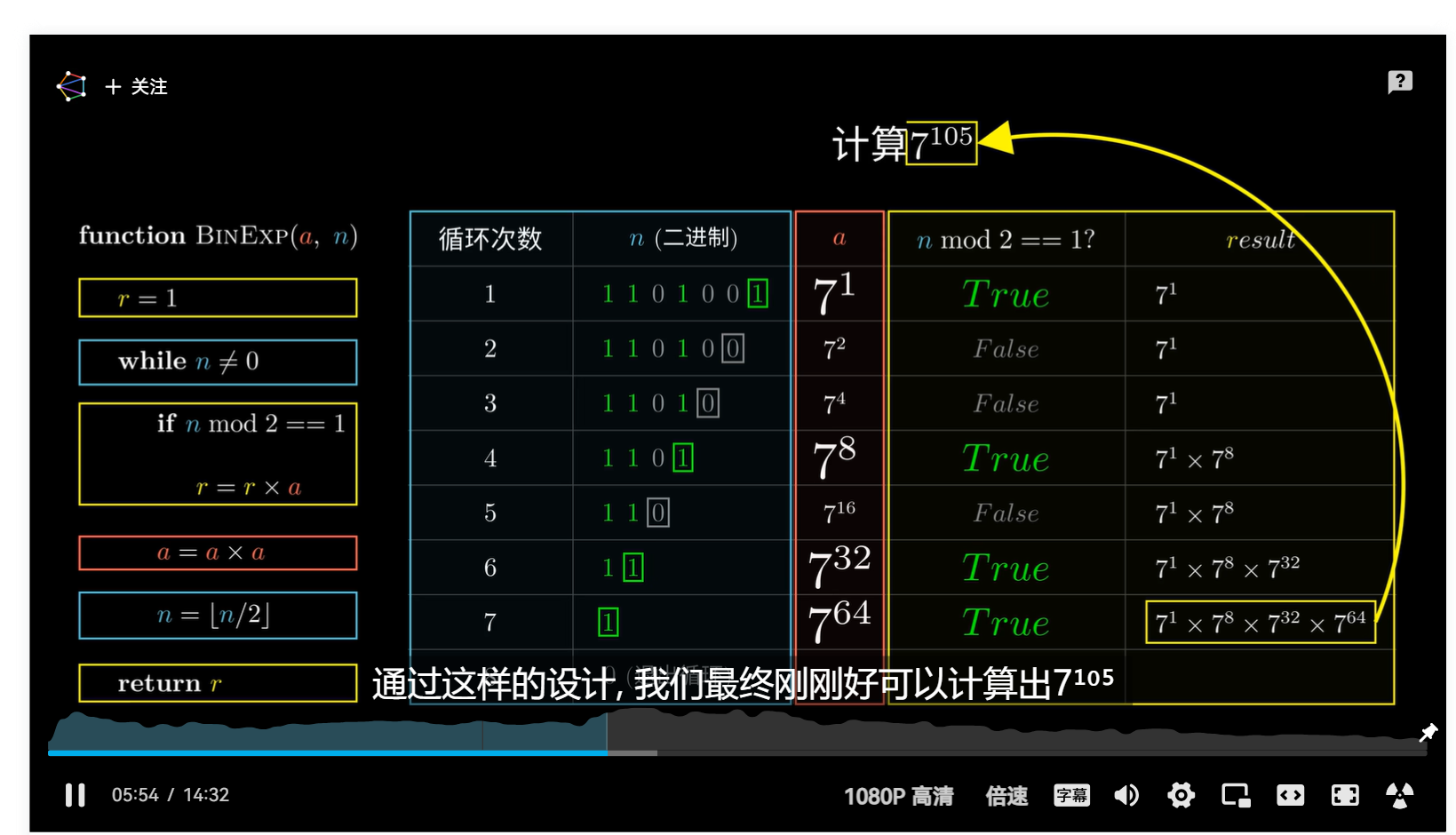
快速幂 https://blog.csdn.net/m0_52072919/article/details/116400820?ops_request_misc=&request_id=&biz_id=102&utm_term=%E5%BF%AB%E9%80%9F%E5%B9%82&utm_medium=distribute.pc_search_result.none-task-blog-2~all~sobaiduweb~default-0-116400820.nonecase&spm=1018.2226.3001.4187
这个博客很好
模板
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/description/877/
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;int n;long long int qmi (long long int base, long long int power, long long int p) long long int result = 1 ; while (power > 0 ) { if (power & 1 ) result = result * base % p; base = base * base % p ; power >>= 1 ; } return result % p; } int main () cin >> n; while (n --){ int base,power,p; cin >> base >> power >> p; cout << qmi (base,power,p)<<endl; } return 0 ; }
n mod 2可以写成n & 1, n/2 可以写成 n >> 1
应用
欧拉(Euler )函数 https://www.acwing.com/solution/content/62556/
证明可用容斥原理
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;typedef long long ll;int main () ll k;cin>>k; while (k--) { ll x; cin>>x; ll res=x; for (ll i=2 ;i<=x/i;i++) if (x%i==0 ) { while (x%i==0 )x/=i; res=res/i*(i-1 ); } if (x>1 )res=res/x*(x-1 ); cout<<res<<endl; } }
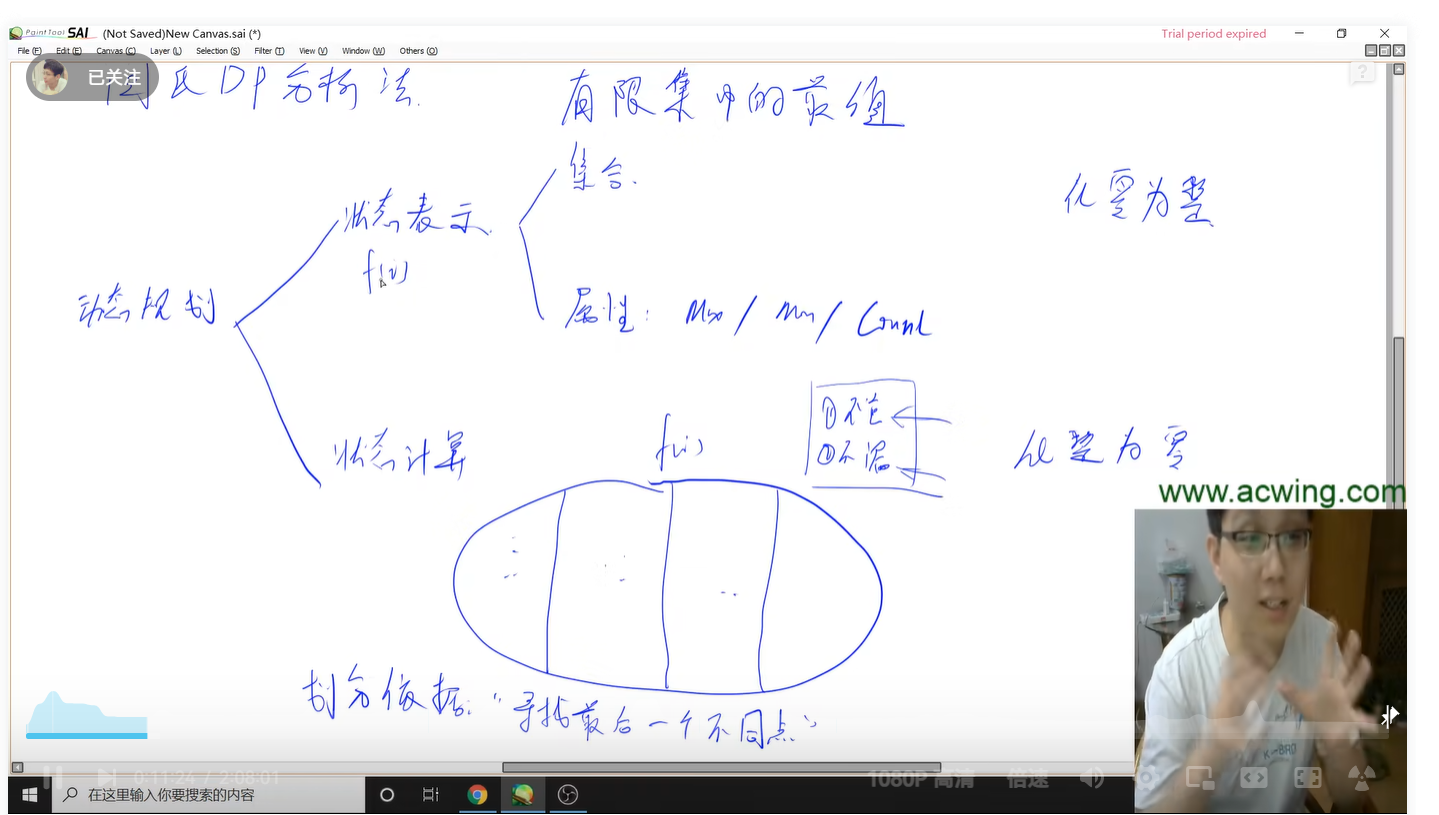
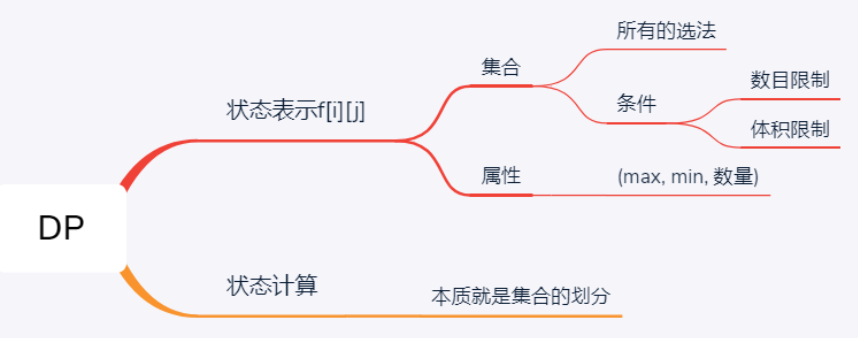
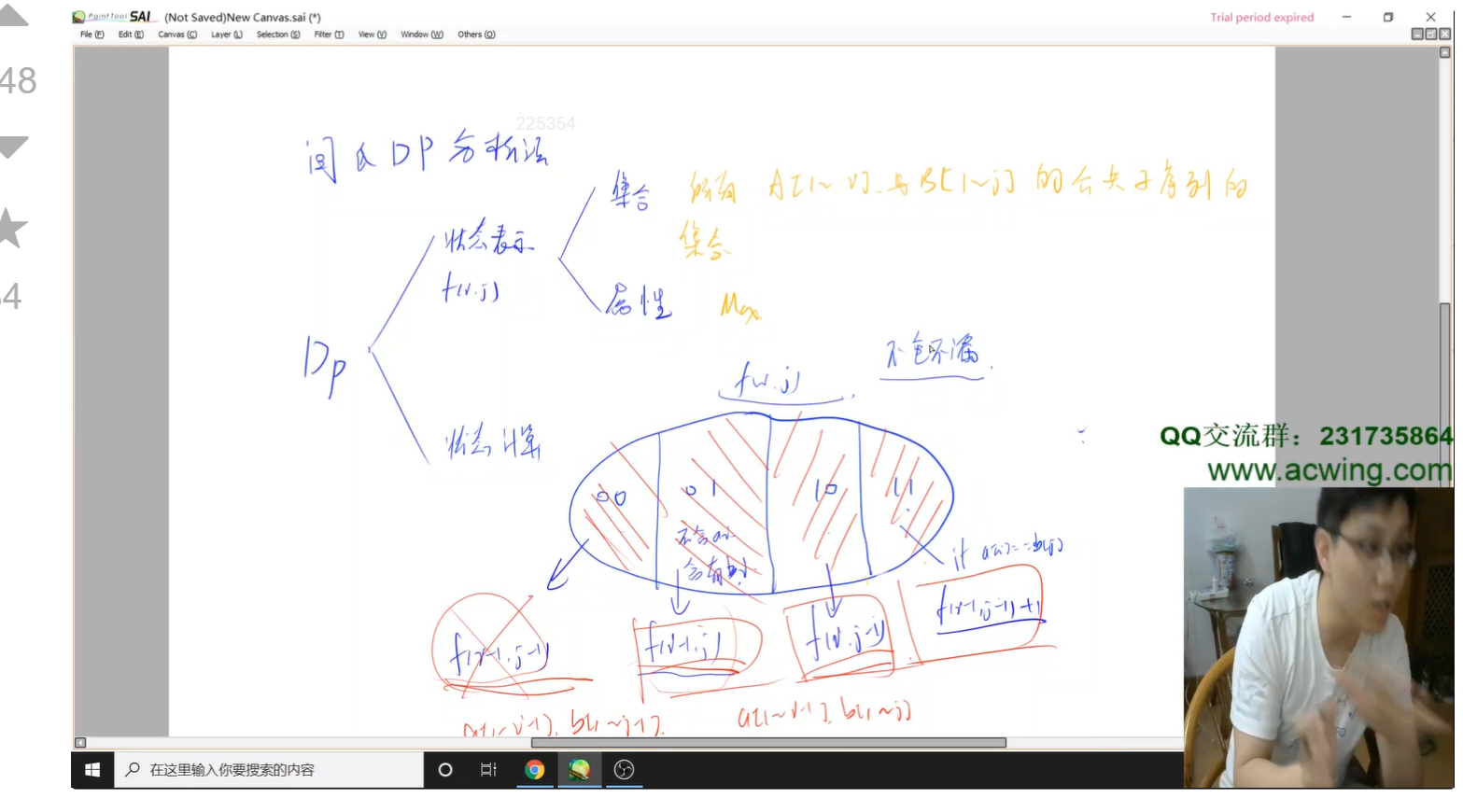
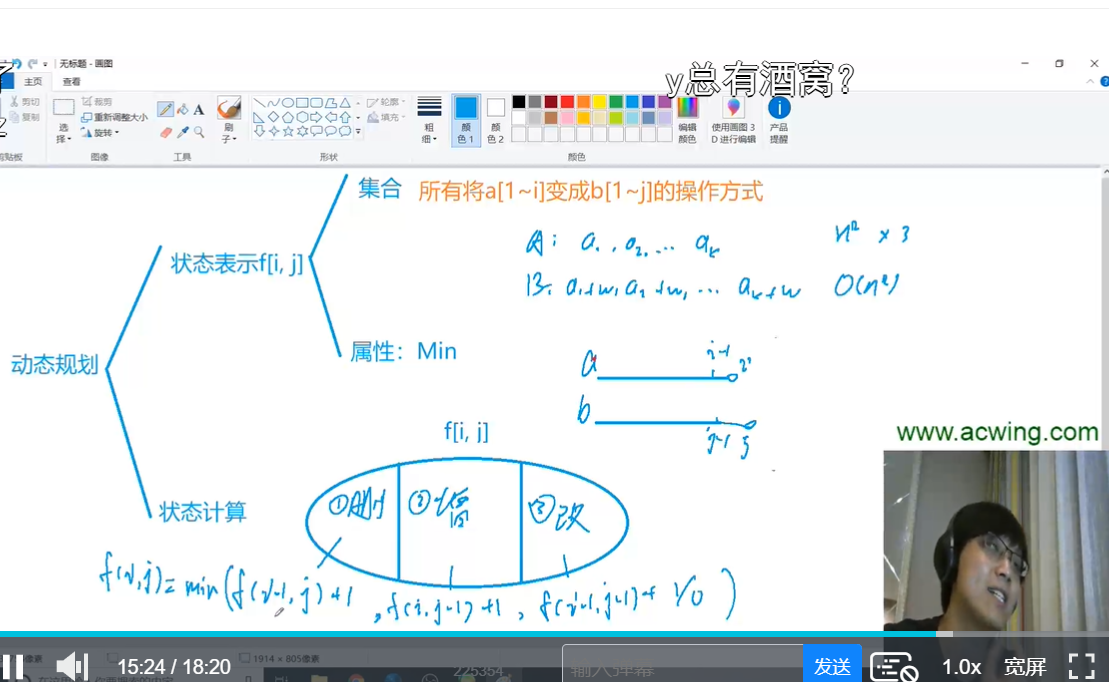
5.第五章 动态规划 闫式DP分析法
从集合角度分析DP问题,求有限集合 的最值/个数..
状态表示:每次划分一个子集 (化零为整) —多做题,刚开始的时候很难想到如何表示,做过类似的题才能大概率写出来
属性:存的是什么东西,max/min/count之类的
状态计算:化整为零
f[i]的子集,不重复,不遗漏(f[i]的全部都被包含),比如取最大值,给每个子集的最大值取个max。
集合划分的套路:寻找最后一个不同点
想学好dp整理好模型很重要,比如选择问题-背包模型,子序列问题-最长上升子序列这种模型
dp很看重经验,(做过类似的题)
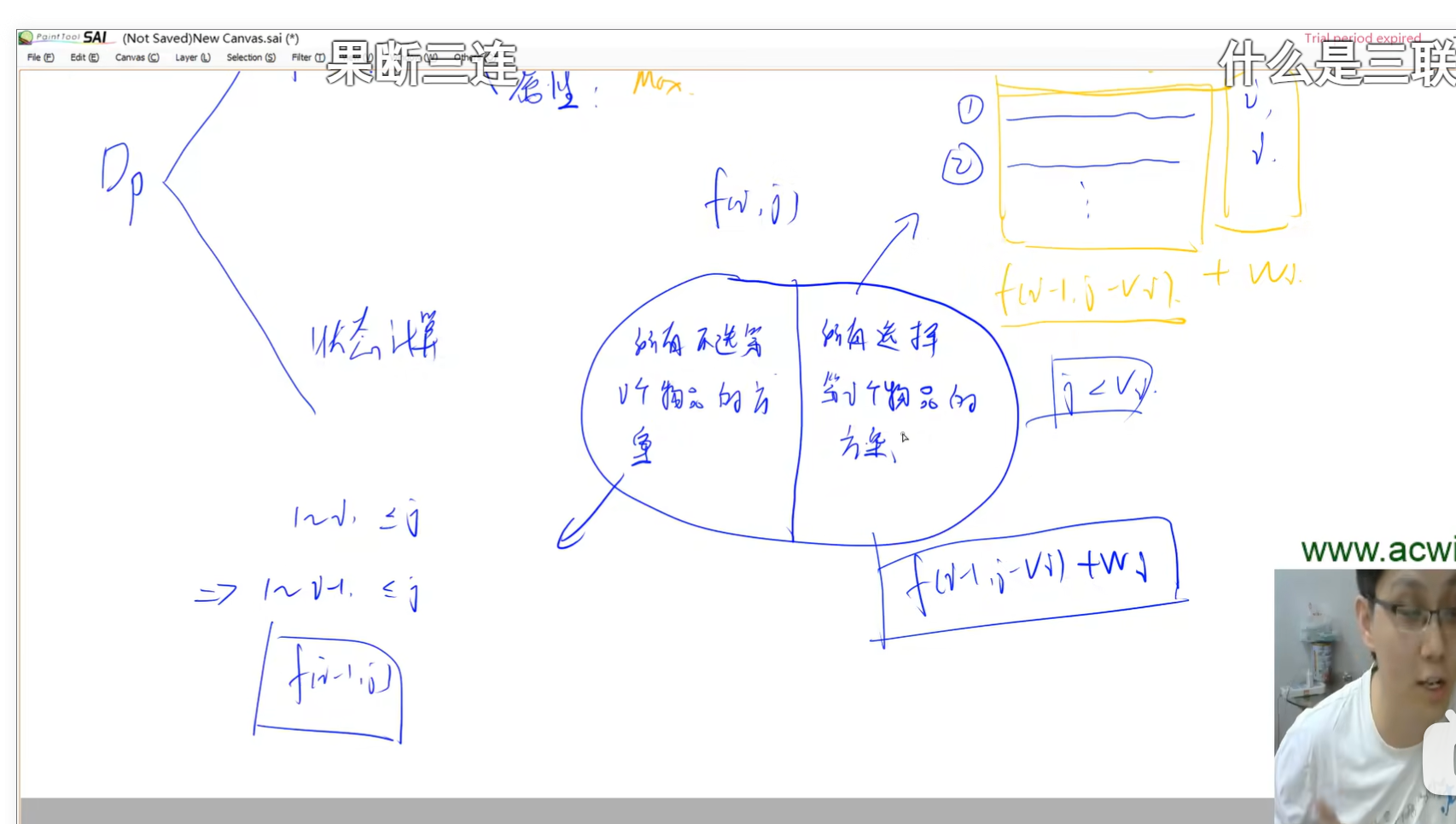
状态表示 f[i,j]
选择物品i的方案不一定存在,要判断j 是否>=v[i]
例题 https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/1214/ 地宫取宝
重复调用的问题适合改动态规划
斐波那契数列优化 1.递归
2.记忆化
3.dp
4.使用两个变量
动态规划就是递推的子集
例题
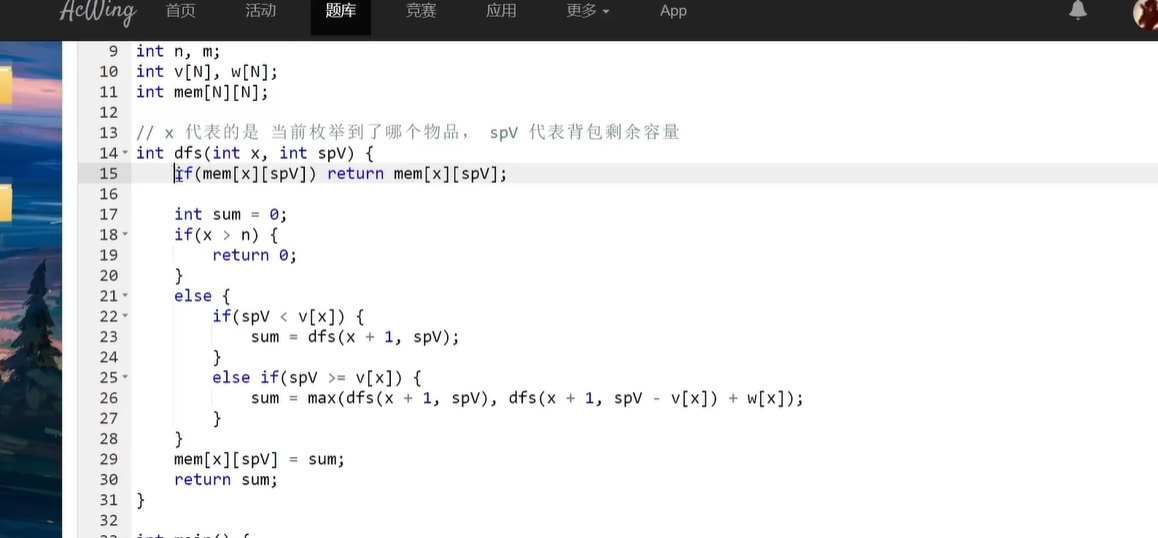
背包问题 01背包问题 一维 01 逆序,完全 正序
记化化搜索
二维DP #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;const int MAXN = 1005 ;int v[MAXN]; int w[MAXN]; int f[MAXN][MAXN]; int main () int n, m; cin >> n >> m; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) cin >> v[i] >> w[i]; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) for (int j = 1 ; j <= m; j++) { if (j < v[i]) f[i][j] = f[i - 1 ][j]; else f[i][j] = max (f[i - 1 ][j], f[i - 1 ][j - v[i]] + w[i]); } cout << f[n][m] << endl; return 0 ; }
滚动数组(优化成一维DP)版本
for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) for (int j = m; j >= 0 ; j--) { if (j < v[i]) f[i][j] = f[i - 1 ][j]; f[j] = f[j]; else f[i][j] = max (f[i - 1 ][j], f[i - 1 ][j - v[i]] + w[i]); f[j] = max (f[j], f[j - v[i]] + w[i]);
完全背包 二维
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;const int P = 1e3 + 10 ;int N,V;int v[P],w[P];int mm[P][P]; int main () cin >> N >> V; for (int i = 1 ; i <= N; i ++){ cin >> v[i] >> w[i]; } for (int i = 1 ; i <= N; i ++){ for (int j = 1 ; j <= V; j ++){ if (j < v[i])mm[i][j] = mm[i - 1 ][j]; else mm[i][j] = max (mm[i - 1 ][j],mm[i][j - v[i]]+ w[i]); } } cout << mm[N][V]; return 0 ; } #include <iostream> using namespace std;const int N = 1010 ;int f[N][N];int v[N],w[N];int main () int n,m; cin>>n>>m; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n ;i ++) { cin>>v[i]>>w[i]; } for (int i = 1 ; i<=n ;i++) for (int j = 0 ; j<=m ;j++) { for (int k = 0 ; k*v[i]<=j ; k++) f[i][j] = max (f[i][j],f[i-1 ][j-k*v[i]]+k*w[i]); } cout<<f[n][m]<<endl; }
一维 可以画图,体积从正序枚举是对的,每个物品可以无限取,从倒序枚举是错的,不然和01(只能取一次)一样了,画个图就ok
#include <iostream> using namespace std;const int N = 1010 ;int f[N];int v[N],w[N];int main () int n,m; cin>>n>>m; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n ;i ++) { cin>>v[i]>>w[i]; } for (int i = 1 ; i<=n ;i++) for (int j = v[i] ; j<=m ;j++){ f[j] = max (f[j],f[j-v[i]]+w[i]); } cout<<f[m]<<endl; }
多重背包
多重背包问题 I (数据范围100,n^3没超1e7-1e8)
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/4/
#include <iostream> #include <algorithm> using namespace std;const int N = 110 ;int v[N], w[N], s[N];int f[N][N];int n, m;int main () cin >> n >> m; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i ++) cin >> v[i] >> w[i] >> s[i]; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i ++){ for (int j = 1 ; j <= m; j ++){ for (int k = 0 ; k <= s[i]; k ++){ if (j >= k * v[i]){ f[i][j] = max (f[i][j], f[i - 1 ][j - k * v[i]] + k * w[i]); } } } } cout << f[n][m] << endl; return 0 ;}
多重背包问题 II (正常做会超)
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/5/
分组背包
二维 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;const int N=110 ;int f[N][N]; int v[N][N],w[N][N],s[N]; int n,m,k;int main () cin>>n>>m; for (int i=1 ;i<=n;i++){ cin>>s[i]; for (int j=0 ;j<s[i];j++){ cin>>v[i][j]>>w[i][j]; } } for (int i=1 ;i<=n;i++){ for (int j=0 ;j<=m;j++){ f[i][j]=f[i-1 ][j]; for (int k=0 ;k<s[i];k++){ if (j>=v[i][k]) f[i][j]=max (f[i][j],f[i-1 ][j-v[i][k]]+w[i][k]); } } } cout<<f[n][m]<<endl; }
一维 因为只用到了第i-1 列,所以可以仿照01 背包的套路逆向枚举体积 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;const int N=110 ;int f[N];int v[N][N],w[N][N],s[N];int n,m,k;int main () cin>>n>>m; for (int i=0 ;i<n;i++){ cin>>s[i]; for (int j=0 ;j<s[i];j++){ cin>>v[i][j]>>w[i][j]; } } for (int i=0 ;i<n;i++){ for (int j=m;j>=0 ;j--){ for (int k=0 ;k<s[i];k++){ if (j>=v[i][k]) f[j]=max (f[j],f[j-v[i][k]]+w[i][k]); } } } cout<<f[m]<<endl; }
二维费用背包 例题 洛谷 1130红牌
例题 https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/description/8/
背包问题的变种
01背包求方案数 例题 acwing278. 数字组合
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;const int N = 1e4 + 10 ;int n,m;int a[N];int f[N][N];int main () cin >> n >>m; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i ++){ cin >> a[i]; } for (int i = 0 ; i <= n+1 ; i++) { f[i][0 ] = 1 ; } for (int i = n; i >= 1 ; i--) { for (int j = 1 ; j <= m; j++) { f[i][j] = f[i + 1 ][j]; if (j >= a[i]) { f[i][j] += f[i + 1 ][j - a[i]]; } } } cout << f[1 ][m]; return 0 ; }
01背包求具体方案 为什么逆序枚举?
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/description/12/
https://blog.csdn.net/yl_puyu/article/details/109960323解释很好
#include <iostream> #include <algorithm> using namespace std;const int N = 1005 ;int n, m;int v[N], w[N];int f[N][N]; int main () cin >> n >> m; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; ++i) cin >> v[i] >> w[i]; for (int i = n; i >= 1 ; --i) for (int j = 0 ; j <= m; ++j) { f[i][j] = f[i + 1 ][j]; if (j >= v[i]) f[i][j] = max (f[i][j], f[i + 1 ][j - v[i]] + w[i]); } int j = m; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; ++i) if (j >= v[i] && f[i][j] == f[i + 1 ][j - v[i]] + w[i]) { cout << i << ' ' ; j -= v[i]; } return 0 ; }
01背包求最优方案数 背包例题
https://www.luogu.com.cn/paste/s2v5pn69
洛谷P1802 5倍经验日(01背包变形问题)
这是一道变了形的01 背包 首先我们因为和每个人打都一定有经验所以一定都要打一遍。 所以不难想到max=lose[1 ]+lose[2 ]......+lose[n]+某些磕了药打赢的多出的经验值 因此我们可以进行一个转换,把价值记为win[i]-lose[i],溶剂就是要打赢磕的药,然后要使价值总和最大,然后就变成了基础的零一背包了。。。 #include <iostream> #include <cstring> #include <string> #include <cmath> #include <algorithm> #include <cstdio> using namespace std;int a[100005 ];long long f[1000005 ];int win[100005 ];int v[100005 ];int lose[100005 ];int main () int n,m; int sum=0 ; scanf ("%d%d" ,&n,&m); for (int i=1 ;i<=n;i++){ scanf ("%d%d%d" ,&lose[i],&win[i],&v[i]); a[i]=win[i]-lose[i]; sum=sum+lose[i]; } for (int i=1 ;i<=n;i++){ for (int j=m;j>=v[i];j--){ f[j]=max (f[j],f[j-v[i]]+a[i]); } } printf ("%lld" ,5 *(f[m]+sum)); return 0 ; }
完全背包求方案数 例题
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/description/1373/
题解:https://www.acwing.com/solution/content/31275/
//和01背包求方案数写法除了改循环条件几乎没区别
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/description/3385/
背包例题 https://www.luogu.com.cn/paste/s2v5pn69
洛谷P1802 5倍经验日(01背包变形问题) 这是一道变了形的01 背包 首先我们因为和每个人打都一定有经验所以一定都要打一遍。 所以不难想到max=lose[1 ]+lose[2 ]......+lose[n]+某些磕了药打赢的多出的经验值 因此我们可以进行一个转换,把价值记为win[i]-lose[i],溶剂就是要打赢磕的药,然后要使价值总和最大,然后就变成了基础的零一背包了。。。 #include <iostream> #include <cstring> #include <string> #include <cmath> #include <algorithm> #include <cstdio> using namespace std;int a[100005 ];long long f[1000005 ];int win[100005 ];int v[100005 ];int lose[100005 ];int main () int n,m; int sum=0 ; scanf ("%d%d" ,&n,&m); for (int i=1 ;i<=n;i++){ scanf ("%d%d%d" ,&lose[i],&win[i],&v[i]); a[i]=win[i]-lose[i]; sum=sum+lose[i]; } for (int i=1 ;i<=n;i++){ for (int j=m;j>=v[i];j--){ f[j]=max (f[j],f[j-v[i]]+a[i]); } } printf ("%lld" ,5 *(f[m]+sum)); return 0 ; }
区间DP 例题 石子合并 https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/description/284/
视频讲解的很好
绝大部分区间dp问题,先枚举区间长度,再枚举区间左端点
状态机DP https://blog.csdn.net/qq_42958831/article/details/130059756
这个博客把灵神的思路讲得很明白
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/description/1059/
题解讲得很好
#include <iostream> #include <cstring> using namespace std;const int N = 1e5 + 10 , M = 110 ;int n, k;int w[N];int f[N][M][2 ];int main () cin >> n >> k; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; ++ i) cin >> w[i]; memset (f, -0x3f , sizeof f); f[0 ][0 ][0 ] = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; ++ i) { for (int j = 0 ; j <= k; ++ j) { f[i][j][0 ] = f[i - 1 ][j][0 ]; if (j) f[i][j][0 ] = max (f[i][j][0 ], f[i - 1 ][j - 1 ][1 ] + w[i]); f[i][j][1 ] = max (f[i - 1 ][j][1 ], f[i - 1 ][j][0 ] - w[i]); } } int res = 0 ; for (int j = 0 ; j <= k; ++ j) res = max (res, f[n][j][0 ]); cout << res << endl; return 0 ; }
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/1058/
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;const int A =1e5 ,B = 10 ,C = 2 , inf = 0x3f3f3f ;int dp[A][B][C];int w[A];int main () int n; cin >> n; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i ++){ cin >> w[i]; } memset (dp, -0x3f , sizeof dp); for (int i = 0 ; i <= 2 ; ++ i) dp[0 ][i][0 ] = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i ++){ for (int j = 0 ; j <= 2 ; j ++){ dp[i][j][0 ] = max (dp[i - 1 ][j][0 ], dp[i - 1 ][j][1 ] + w[i]); dp[i][j][1 ] = dp[i - 1 ][j][1 ]; if (j)dp[i][j][1 ] = max (dp[i][j][1 ], dp[i - 1 ][j - 1 ][0 ] - w[i]); } } int ans = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i <= 2 ; i ++){ ans = max (dp[n][i][0 ],ans); } cout << ans; }
树形DP https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV17o4y187h1/?spm_id_from=333.337.search-card.all.click&vd_source=4452cbcad134fb17ec9cfb03a0acbdac 树的直径讲解
例题见视频下方链接
https://www.cnblogs.com/RioTian/p/15163878.html 博客
卡特兰数
https://leetcode.cn/circle/discuss/lWYCzv/
例题1 进出栈序列
线性DP 最长上升子序列I 算法1
状态表示:f[i]表示从第一个数字开始算,以w[i]结尾的最大的上升序列。(以w[i]结尾的所有上升序列中属性为最大值的那一个)
状态计算(集合划分):j∈(0,1,2,..,i-1), 在w[i] > w[j]时,
最后在找f[i]的最大值。
时间复杂度
#include <iostream> using namespace std;const int N = 1010 ;int n;int w[N], f[N];int main () cin >> n; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) cin >> w[i]; int mx = 1 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { f[i] = 1 ; for (int j = 0 ; j < i; j++) { if (w[i] > w[j]) f[i] = max (f[i], f[j] + 1 ); } mx = max (mx, f[i]); } cout << mx << endl; return 0 ; }
算法2
我认为可以延伸到求满足某个性质的一个子序列
最长上升子序列II (数据范围n<1e5) 这题解法特别好
https://www.acwing.com/solution/content/2192/ 题解讲得很清楚接龙序列
最长公共子序列
状态计算可能有重复,只要不越界不遗漏就ok
编辑距离
有f[i-1]基本i都要从1开始遍历
https://www.acwing.com/activity/content/problem/content/1094/
状态压缩DP 例题 https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P8687
图上动态规划 日期问题 https://blog.51cto.com/u_15656645/5373606 蓝桥 日期问题模板
闰年要被4整除并且不能被100整除或者能被400整除
(year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0 )||(year % 400 == 0)
https://www.acwing.com/activity/content/problem/content/9436/
https://www.acwing.com/blog/content/24163/题解大合集
https://www.acwing.com/solution/content/37448/ 这个代码的流程很好,可以当模板
贡献法 https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_46239370/article/details/115262482 蓝桥杯 子串分值和 用到乘法原理和贡献法,题解很好



 S[i, j] = 第i行j列格子左上部分所有元素的和
S[i, j] = 第i行j列格子左上部分所有元素的和